Open-source large language models (LLMs) offer compelling alternatives to commercial solutions. They offer the advantages of cost efficiency, customization through fine-tuning, and the flexibility to run locally or on private servers, ensuring full control over data and infrastructure.
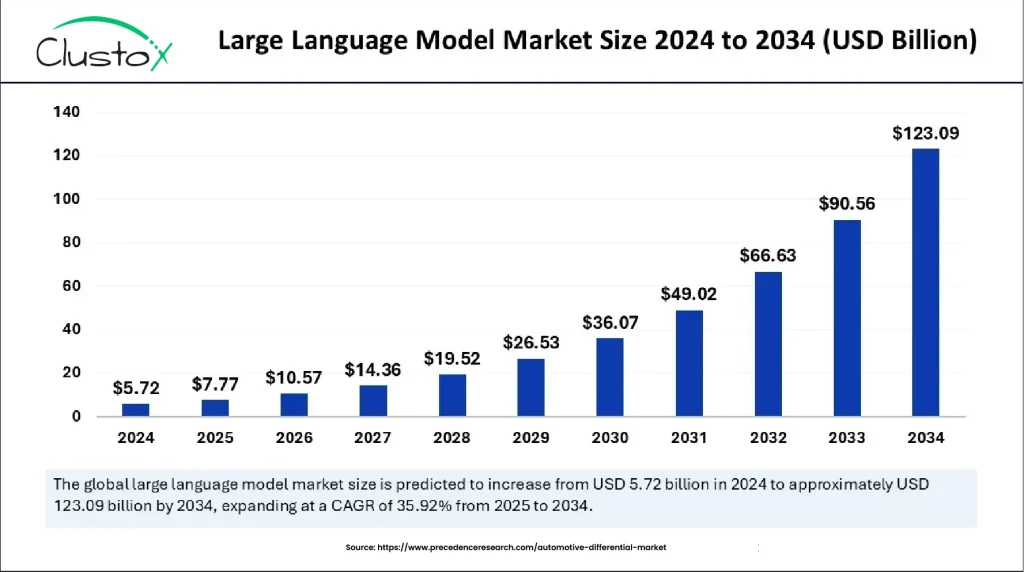
The LLM market is projected to grow from $7.77 billion in 2025 to $123.09 billion by 2034, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 35.92%.
However, with so many options available, which one should you choose?
This article presents the leading open-source LLMs that outperform the majority of others in both capability and accessibility.
However, before moving towards the top 10 open source LLMs, let’s first understand what a large language model is, how they work, and the
common applications and limitations of LLMs.
What Is a Large Language Model (LLM)?
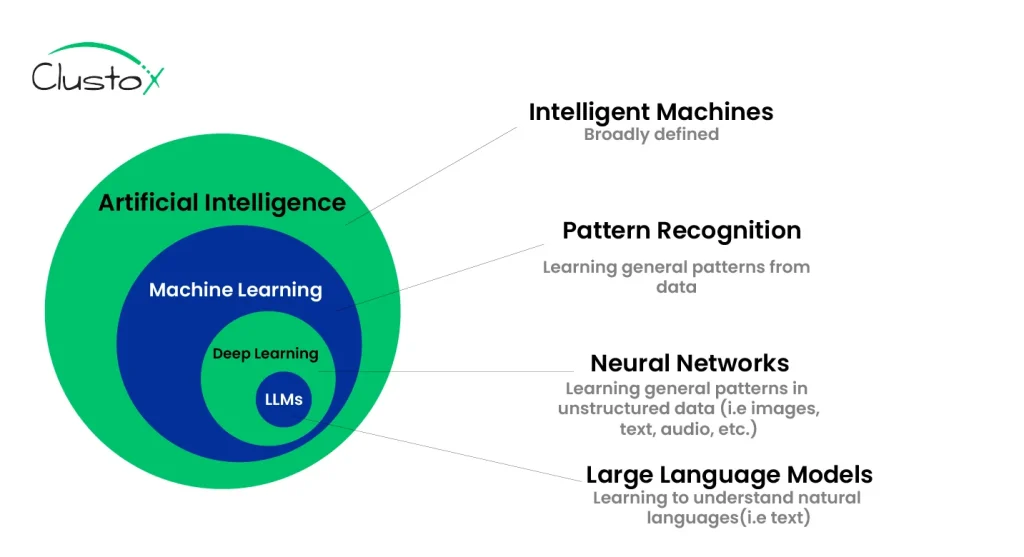
A large language model (LLM) is an artificial intelligence system designed to generate and understand human-like text. These models form the core of AI chatbots, writing assistants, automated summarizers, and other language-based applications.
At their core, open source LLMs for natural language processing take a text prompt. They generate a contextually appropriate response, not by searching for keywords or predefined templates but by predicting the next most likely words based on vast training data. This allows them to respond dynamically to various queries with coherent, context-aware output.
Table of Contents
LLMs have become popular because of their versatility. A single model can be adapted (with or without additional fine-tuning) to perform tasks such as:
- Answering customer support questions
- Drafting emails and marketing copy
- Summarizing meetings or articles
- Assisting in coding or data analysis
How Do LLMs Work?
Early language models, such as GPT-1, struggled to maintain coherence beyond a few sentences. In contrast, modern models like GPT-4o can generate thousands of words of fluent, contextually relevant text. This dramatic improvement is largely due to advancements in training scale, architecture, and data quality.
AI chatbot development also improves customer engagement. These chatbots are popular on platforms like ChatGPT, Google Gemini, and open-source alternatives for interactive dialogue.
To achieve their capabilities, LLMs are trained on vast datasets, typically including a combination of publicly available internet text, books, academic papers, news articles, and sometimes even synthetic data generated by previous models. While the exact datasets differ between developers (and may depend on licensing considerations), the goal is consistent: expose the model to diverse language patterns across various topics and styles.
The training involves feeding this text data into a neural network and teaching the model to predict the next word in a sequence. Over time, it learns statistical relationships between words, phrases, and concepts. These relationships are represented in high-dimensional vector spaces, where semantically similar tokens are located near each other.
At the heart of an LLM is a transformer-based neural network, which uses layers of self-attention mechanisms to weigh the importance of different words in context. Instead of memorizing answers, the model develops a probabilistic understanding of language structure, enabling it to generate coherent responses to prompts it has never seen before.
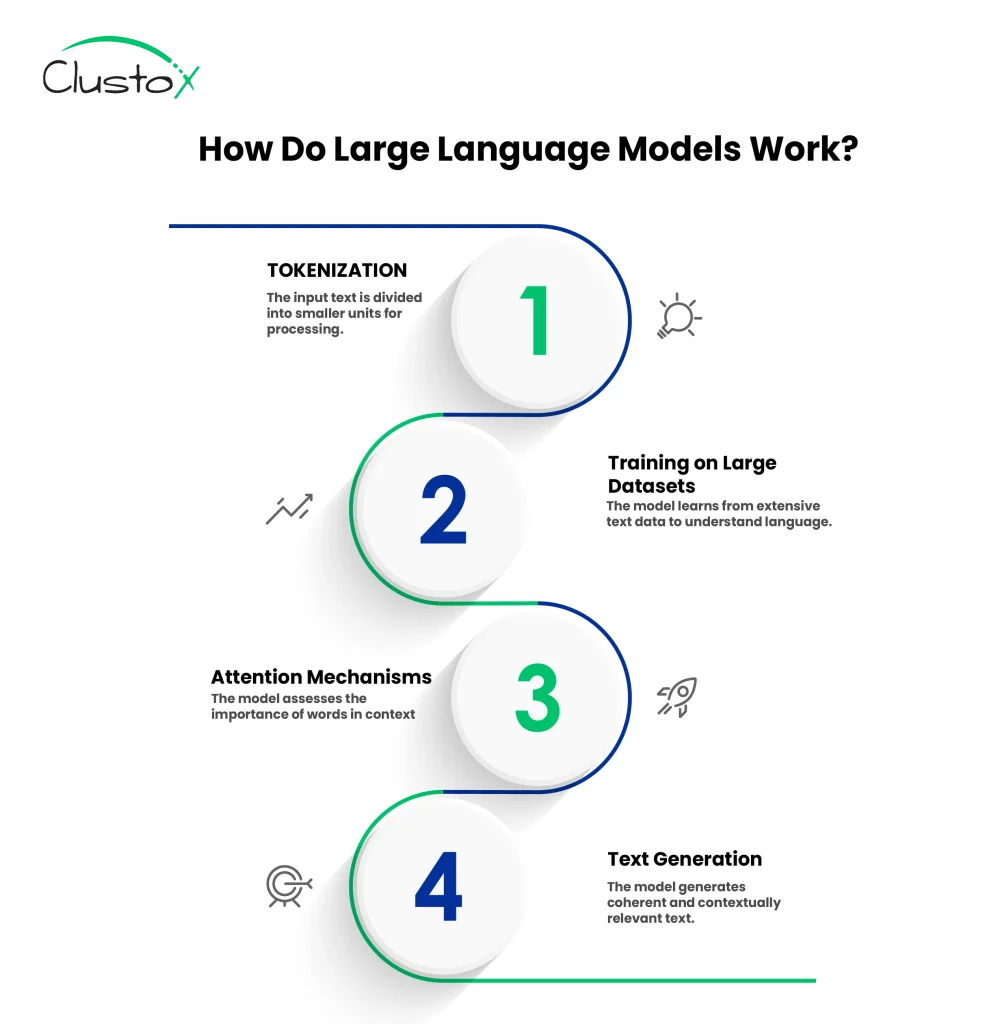
In short, an LLM works as generative AI; it doesn’t “know” facts the way humans do, but it’s exceptionally good at generating responses that appear informed, thanks to its exposure to billions of linguistic patterns during training.
Struggling with high costs and limited control over proprietary models? It’s time to switch to open-source LLMs to drive your AI projects forward.
1. DeepSeek R1

DeepSeek R1 is one of the best open source large language models from DeepSeek AI, built to handle tasks requiring logic, real-time decisions, and step-by-step analytical processes. It stands out for its ability to transparently explain its conclusions, making it ideal for high-stakes or technical work.
DeepSeek R1 is a reasoning-optimized language model purpose-built for logical inference, technical tasks, and multi-domain problem-solving. It’s particularly effective in scientific documentation and structured reasoning workflows.
Release Date: April 2024
Parameter Size: 236B (DeepSeek-V2 also exists)
Developer: DeepSeek AI (China)
| Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Reasoning Focus | Excels in logic-heavy and mathematical tasks |
| Model Architecture | Mixture of Experts (MoE) for efficient querying |
| Context Window | Supports up to 128K tokens |
| Language Support | Over 20 languages |
| Use Cases | Research, document analysis, and technical content |
2. Qwen2.5-72 B-Instruct
Built by Alibaba’s DAMO Academy, it is at the top of the 2025 open source LLM rankings. This model is designed for instruction-following and excels in multilingual settings, programming, and structured output generation.
From Alibaba’s DAMO Academy, Qwen2.5-72B is a highly scalable instruction-tuned LLM ideal for structured output, mathematical reasoning, and multilingual applications.
Release Date: Ongoing releases since 2023
Parameter Size: 0.5B to 72B (Qwen-72B is largest)
Developer: Alibaba DAMO Academy
| Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Parameter Count | 72.7B (70B core parameters) |
| Architecture | RoPE, SwiGLU, RMSNorm, QKV Attention Bias |
| Languages | 29+ supported |
| Output Format | JSON and structured text |
| Best For | Coding, education, and content generation |
3. Llama 4

Meta’s LLaMA 4 builds upon the strengths of its predecessor, delivering enhanced performance in dialogue understanding and general-purpose reasoning. As one of the most capable open-source LLMs available, it is optimized for developers seeking scalable, multilingual solutions across diverse domains.
With refined instruction tuning and extended context capabilities, LLaMA 4 excels in long-form conversations and complex multilingual tasks. Its architecture is engineered for efficiency and adaptability, making it a robust choice for real-world applications ranging from virtual assistants to enterprise-level automation.
Release Date: April 18, 2024
Parameter Size: 8B and 70B
Developer: Meta AI
| Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Performance | Strong across reasoning and knowledge tasks |
| Resource Usage | Suitable for better efficiency |
| Context Window | 128K tokens |
| Supported Languages | 8+ major languages |
| Community Support | Extensive documentation |
4. Mistral-Large-Instruct-2407
Mistral-Large is one of the leading open-source LLMs built with 123 billion parameters for high accuracy across natural language tasks. It includes native function calling and performs well in code generation and knowledge retrieval.
A state-of-the-art dense LLM with 123B parameters, Mistral-Large is perfect for low hallucination, native function calls, and broad language coverage, making it ideal for high-accuracy enterprise use.
Release Date: September 27, 2023
Parameter Size: 7B
Developer: Mistral AI
| Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Parameter Count | 123B |
| Output Capability | JSON and API interaction |
| Long Context | 131K tokens |
| Accuracy | Low hallucination rate |
| Ideal Use | Customer service, technical content, marketing |
5. Claude
Claude is a family of large language models developed by Anthropic, an AI safety-focused company founded by former OpenAI researchers. Named after Claude Shannon, the father of information theory, the Claude models emphasize helpfulness, honesty, and harmlessness (HHH).
Since their debut in 2023, Claude models have evolved rapidly, with releases improving in reasoning, speed, context handling, multimodality, and cost-efficiency. Claude 3.5 Sonnet and Claude 3.7 Sonnet represent the cutting edge of this progression, aiming to challenge leading models from OpenAI and Google.
Release Date: July 11, 2023
Parameter Size: Approximately 137 billion parameters
Developer: Anthropic
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Expanded Context Understanding | Enhanced ability to process and understand longer conversations and documents. |
| Language Support | Multilingual |
| Improved Performance Metrics | Demonstrated significant improvements in various AI benchmarks compared to its predecessors. |
| Applications | Text generation, coding, analysis, and customer support |
6. Phi-4
Phi-4 by Microsoft proves that smaller models can achieve great results when used correctly. It delivers strong reasoning and programming performance without heavy hardware requirements.
Developed by Microsoft, Phi-4 proves that compact models can still deliver. It’s particularly well-suited for low-resource deployments where the performance-to-size ratio is crucial.
Release Date: May 2024
Parameter Size: Not officially disclosed, likely small (<10B)
Developer: Microsoft Research
| Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Model Size | Lightweight but highly capable |
| Specialization | Code generation, logic tasks |
| Deployment | Runs on consumer-grade hardware |
| Use Cases | Edge AI, mobile apps, local inference |
7. Gemma-2-9b-it
Google’s Gemma-2-9b-it model offers a compact, instruction-tuned alternative perfect for reasoning and deployment on resource-constrained systems. It inherits design elements from Gemini research.
Built by Google and inspired by Gemini research, Gemma-2-9B-it balances compact design with impressive reasoning and summarization skills. It is best for edge devices and instruction adherence.
Release Date: February 21, 2024
Parameter Size: 2B and 7B
Developer: Google DeepMind
| Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Parameter Count | 9B |
| Efficiency | Quantized for reduced memory/GPU load |
| Attention Mechanism | Hybrid: local + global attention |
| Instruction Following | High precision |
8. Falcon 180B
Falcon 180B is one of the leading open-source LLMs, built with 180 billion parameters and trained on a vast 3.5 trillion-token dataset. Developed by the Technology Innovation Institute, it’s perfect for research and commercial use.
It performs exceptionally well in logic-intensive and coding scenarios while maintaining efficiency in deployment despite its massive scale.
Release Date: September 6, 2023
Parameter Size: 180B
Developer: Technology Innovation Institute (TII), UAE
| Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Model Size | 180 billion parameters |
| Training Dataset Size | 3.5 trillion tokens |
| Architecture | Dense Transformer |
| Primary Language | English |
| License | Open-source (commercial and research use allowed) |
| Context Length | Not officially disclosed |
| Strengths | Reasoning, code generation, and high benchmark scores |
| Efficiency | Best for better deployment scalability |
| Developed By | Technology Innovation Institute (TII), UAE |
9. Vicuna 13B

Vicuna 13B is a fine-tuned LLM, best for dialogue. It stands out for producing remarkably human-like conversations and is designed to serve as a conversational layer over open-source base models like LLaMA.
With a parameter size of 13 billion, it offers a compelling balance between quality and resource efficiency.
Release Date: March 2023
Parameter Size: B, 13B (fine-tuned LLaMA)
Developer: LMSYS (UC Berkeley, CMU, Stanford, UCSF)
| Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Model Size | 13 billion parameters |
| Architecture | Based on LLaMA, dense transformer |
| Primary Use Case | Conversational applications |
| Language Support | English |
| License | Open-source (non-commercial use encouraged) |
| Training Focus | Dialogue quality and coherence |
| Strengths | Natural-sounding responses, lightweight inference |
| Community Feedback | High praise for friendliness and coherence |
| Developed By | LMSYS (UC Berkeley, CMU, Stanford, and UC San Diego) |
10. Mixtral 8x22B
Mixtral 8x22B is a Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) model and is one of the leading open-source LLMs, created by Mistral AI. While it contains 141 billion parameters in total, only 39 billion are active at any time, resulting in excellent performance at significantly reduced computational costs.
It is multilingual and has demonstrated top-tier results in programming and mathematics benchmarks.
Release Date: December 11, 2023
Parameter Size: 12.9B (Mixture of Experts, 2 of 8 active)
Developer: Mistral AI
| Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Model Size | 141 billion parameters (39 billion active per query) |
| Architecture | Mixture-of-Experts (8 experts, 2 active) |
| Language Support | English, French, Italian, Spanish |
| License | Open-source |
| Strengths | Code generation, mathematical reasoning, and efficiency |
| Context Length | Not officially disclosed |
| Benchmarks | Strong performance in MBPP (Python coding tasks) |
| Developed By | Mistral AI |
Open Source LLMs In 2025: A Deep Technical Review
The table below presents a detailed open source LLM comparison for 2025 of the leading open-source language models available in 2025. The table outlines their technical specifications, language support, performance capabilities, and the types of tasks they handle best, helping you choose the right model based on your project’s scale, domain, and deployment needs.
| Model | Parameters | Architecture | Context Length | Strengths | Developer | License |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DeepSeek R1 | Not disclosed (100B est) | Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) | 128K tokens | Advanced reasoning, technical knowledge, step-by-step logic | DeepSeek AI | Open-source |
| Qwen2.5-72B-Instruct | 72.7B (70B core) | RoPE, SwiGLU, RMSNorm | 128K tokens | Multilingual, structured output (JSON), math & coding | Alibaba DAMO Academy | Open-source |
| Llama 4 | 70B | Transformer based decoder-only architecture | Up to 128,000 tokens | High accuracy on reasoning and language tasks; competitive with GPT-4; multilingual support. | Meta AI | Open-source for research and commercial use |
| Mistral-Large-Instruct-2407 | 123B | Dense Transformer | 131K tokens | Low hallucination, excellent reasoning, JSON support | Mistral AI | Open-source |
| Claude | 70–100B or more | Transformer based model with proprietary enhancements by Anthropic | Up to 200,000 tokens | Exceptional reasoning, safety alignment, few-shot learning, long-context comprehension | Anthropic | Closed-source, available via API and integrations |
| Phi-4 | Not disclosed (13B est) | Compact Transformer | Not disclosed | Small size, efficient reasoning, strong coding | Microsoft | Open-source |
| Gemma-2-9b-it | 9B | Dense Transformer | Not disclosed | Lightweight, mobile-ready, instruction following | Open-source | |
| Falcon 180B | 180B | Dense Transformer | Not disclosed | Reasoning, code generation, and scalable deployment | TII (UAE) | Open (commercial use) |
| Vicuna 13B | 13B | LLaMA-based Transformer | Not disclosed | Human-like chat, conversational AI | LMSYS | Open (non-commercial) |
| Mixtral 8x22B | 141B (39B active) | MoE (8 experts, 2 active) | Not disclosed | Efficient coding, multilingual, and math reasoning | Mistral AI | Open-source |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Which Open Source LLM Is Best For Developers In 2025?
In 2025, Mistral and Mixtral are widely considered the best open-source LLMs for developers due to their top-tier performance, efficient architecture, and fully permissive Apache 2.0 license.Their strong reasoning and lightweight deployment make them ideal for various real-world applications.
How Do Open Source LLMs Differ From Proprietary LLMs?
Open-source LLMs provide access to model weights, code, and often training data, allowing full customization and self-hosting. In contrast, proprietary LLMs are closed-source, typically hosted by providers, and restrict access, usage, and fine-tuning.
What Are The Advantages Of Using Open Source LLMs?
Advantages of using open-source LLMs include full customization, lower cost, on-premise deployment for data privacy, transparency, community support, and freedom from vendor lock-in. They also allow for reproducible research, rapid experimentation, and easier integration into existing systems without restrictive licensing constraints.
How To Choose The Right Open Source LLM For AI Projects?
To choose the right open-source LLM for AI projects, consider your use case (e.g., chat, coding, RAG), required model size, license compatibility, hardware resources, language support, and benchmark performance. Additionally, evaluate the model's community activity, documentation quality, ease of fine-tuning, and availability of tooling and inference frameworks.
Conclusion
The current wave of one of the leading open-source LLMs offers flexibility, cost-efficiency, and immense potential for developers and businesses. From understanding how LLMs work to exploring the limitations and comparing the top models, it’s clear that choosing the right LLM for your needs is essential to meet innovation and success.
If you want to integrate an LLM into your existing infrastructure or explore new AI opportunities, the right model can bring unprecedented capabilities. However, navigating through the complexity of open-source LLMs can be daunting without the right expertise.
This is where a trusted partner in AI and machine learning development can guide you in selecting and implementing the perfect open-source LLM for your projects.
Feel like you’re hitting roadblocks with your AI development? Let’s work together to overcome these challenges and start transforming your AI approach!







Share your thoughts about this blog!