Deploying machine learning models can feel straightforward during development, yet they often become challenging once they move into production. Teams frequently encounter unexpected errors, slow performance, or unstable predictions, disrupting operations.
But why do so many projects struggle at this stage?
Studies indicate that nearly 70% of ML projects never reach full production, mainly due to gaps in deployment practices and operational workflows.
Integrating DevOps for ML deployment provides a structured approach that connects development, operations, and machine learning workflows. Applying DevOps principles ensures stable, scalable, and reliable ML production deployments.
This blog covers how to deploy machine learning models using DevOps, including testing in production, monitoring performance, and applying safe rollback strategies.
Let’s get started by exploring how DevOps can improve ML model deployment!
How Can DevOps Improve Machine Learning Model Deployment?
DevOps strengthens ML deployment by aligning development, operations, and data workflows. This approach helps teams deliver models faster, with fewer errors, and with more predictable performance in production.
Companies often combine these practices with professional ML Development Services to accelerate implementation and ensure adherence to best practices throughout the ML lifecycle.
Table of Contents
Here’s how DevOps improves ML model deployment:
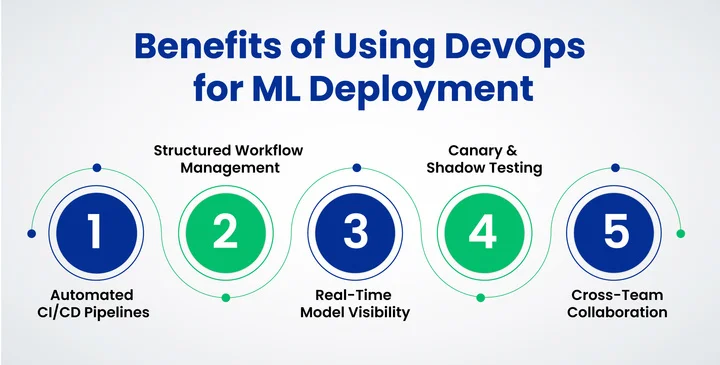
- Faster, More Reliable Releases: CI/CD pipelines automate the build, test, and validation of ML models, reducing manual work and speeding up deployments.
- Consistent and Stable Deployments: Structured workflows ensure updates to code, model artifacts, or data pipelines follow the same checks, preventing disruptions in production.
- Real-Time Visibility Into Model Behavior: Integrated monitoring tools track prediction quality, latency, and system performance, helping teams detect issues early.
- Safer Model Update: Techniques such as canary and shadow deployments allow teams to test new models with limited traffic before a full rollout.
- Better Collaboration Across Teams: Shared pipelines and automated processes align data scientists, DevOps engineers, and operations teams, reducing communication gaps.
This combination of speed, stability, and monitoring ensures ML models remain reliable and effective throughout their lifecycle.
Next, we’ll look at how to test machine learning models in production to confirm they perform reliably under real-world conditions.
What is the Best Way to Test Machine Learning Models in Production?
Models often behave differently in real-world traffic, so production testing helps confirm that predictions remain accurate, stable, and reliable.
Common Strategies For Testing ML Models In Production are:
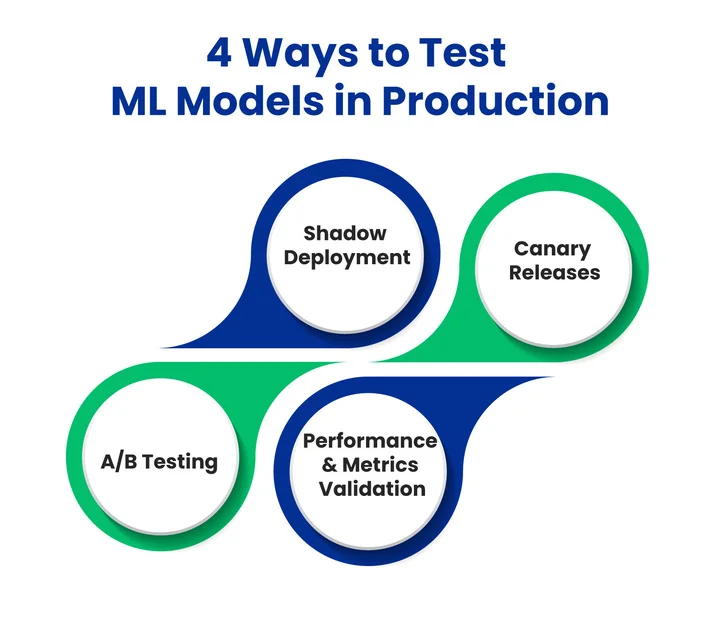
1. Shadow Deployment
The new model runs alongside the existing version without affecting users. Teams compare outputs to identify gaps, performance issues, or unexpected behavior.
2. Canary Releases
A small percentage of traffic (for example, 5–10%) goes to the new model first. This controlled rollout helps detect issues early before a full release.
3. A/B Testing
A/B testing splits traffic between the old and new models, enabling a direct comparison of outcomes. This method helps determine whether the new model improves accuracy, engagement, or other key metrics.
During production testing, it’s essential to track metrics that indicate model performance and reliability, including:
- Accuracy, Precision, and Recall: Are predictions correct and meaningful?
- Latency: Is the model responding quickly enough for its intended use?
- Resource Utilization: How much CPU, GPU, or memory does the model consume?
- Error Rates and Anomalies: Are there unexpected behaviors or spikes in errors?
Here are some practical tips to make production testing more effective:
- Start with a subset of live data before full deployment.
- Automate testing pipelines to ensure consistency and repeatability using professional DevOps services.
- Log all predictions and results for analysis and continuous improvement.
Testing ML models in production is a significant step that confirms they perform well under real-world conditions.
Struggling with ML model deployments? Our DevOps experts organize your CI/CD pipelines, automate testing, and secure reliable releases.
Once testing shows the model is reliable, continuous monitoring ensures it maintains accuracy and adapts to changing data over time.
How are Machine Learning Models Monitored in Production?
Deploying a model is just the beginning. Continuous monitoring ensures it performs reliably, adapts to changing data, and delivers consistent value. Without monitoring, even a well-tested model can degrade over time, leading to inaccurate predictions or system failures.
In healthcare applications, combining ML monitoring with structured EHR software development practices ensures patient data and critical workflows remain accurate, secure, and compliant.
Critical Areas to Monitor in Production:
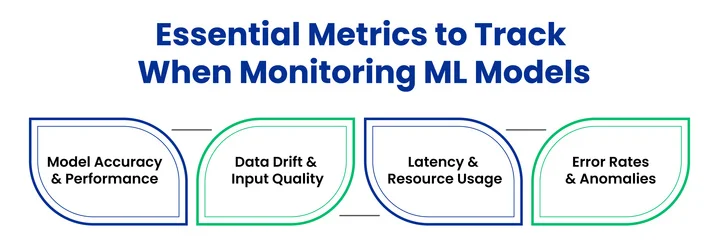
1. Model Accuracy and Performance
Track metrics such as precision, recall, F1 Score, or mean squared error, depending on the model type. This helps identify when the model starts making incorrect predictions.
2. Data Drift and Input Quality
Monitor incoming data for shifts in patterns or distributions that differ from those in the training data. Unexpected changes in input can reduce model accuracy.
3. Latency and Resource Usage
Keep an eye on response times and resource consumption (CPU, GPU, memory). High latency or resource spikes may indicate performance issues.
4. Error Rates and Anomalies
Logging errors, failed predictions, or unusual outputs can help detect problems early and prevent them from affecting users.
Best Practices for Monitoring:
- Set up automated alerts for critical metrics when thresholds are breached.
- Use dashboards to visualize real-time model performance and trends.
- Regularly review logs to identify patterns and optimize the model or data pipeline.
Monitoring is the backbone of maintaining reliable ML deployments. In healthcare applications, combining this monitoring with structured healthcare mobile app development practices ensures that apps remain accurate and secure and deliver consistent value to patients.
After establishing monitoring, teams must also plan for safe rollback strategies in case issues arise.
How Can You Safely Roll Back Machine Learning Models in Production?
Machine learning models in production can sometimes behave unexpectedly. Sudden drops in accuracy, data drift, or system errors make robust rollback strategies for ML models a critical part of any DevOps machine learning pipeline.
Proper rollbacks allow teams to quickly revert to a stable model version, minimizing downtime and maintaining service reliability.
Effective Rollback Strategies in ML Deployment:

1. Version Control for ML Models
Maintaining detailed model versioning ensures that any update can be safely reversed. Tools like MLflow, DVC, or cloud-native solutions (AWS SageMaker, Azure ML) track model artifacts, training data, and metadata. This aligns with ML model deployment strategies that prioritize reproducibility and reliability.
2. Automated Rollback in ML Systems
Integrating automated rollback mechanisms into CI/CD pipelines enables a fast response to performance drops.
For Example, if monitoring detects reduced accuracy or increased latency, the pipeline can automatically redeploy the last stable model. This approach aligns with DevOps practices throughout the ML lifecycle and ensures safe, predictable updates.
3. Shadow and Canary Rollbacks
- Shadow Rollback: Run the previous stable model alongside the new one without affecting users.
- Canary Rollback: Gradually redirect a small subset of traffic to the stable model first.
Both methods reduce risks and validate real-world performance before a full-scale rollback.
4. Testing Rollback Procedures
Regularly testing machine learning models in production for rollback scenarios ensures the procedures work as expected. Simulated incidents in staging environments provide insights into potential failures and strengthen confidence in enterprise ML deployment services.
5. Monitoring During Rollbacks
Continuous monitoring of ML models in production is essential even during rollback. Track metrics such as accuracy, latency, error rates, and resource usage using machine learning monitoring tools.
Proper logging creates an audit trail and supports long-term optimization in cloud-based ML deployment with DevOps.
Implementing these practices makes your DevOps for ML deployment more resilient. Teams can safely update models, scale efficiently, and maintain high reliability under real-world conditions.
Automated rollback, combined with monitoring and structured pipelines, ensures a smooth and secure production environment.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
2. What are the Best Rollback Strategies for ML Models In Production?
Rollback strategies are critical for safe production deployments. Common approaches include:
- Version Control: Maintain previous stable model versions for quick reversion
- Automated Rollbacks: Triggered via CI/CD pipelines when metrics fall below thresholds
- Shadow or Canary Rollbacks: Gradual redirection of traffic to test the stable model
Regular testing of rollback procedures and logging helps ensure reliability and minimize downtime.
3. How Do You Ensure ML Model Performance Over Time?
Ensuring consistent ML model performance requires a combination of monitoring and proactive management:
- Track metrics such as accuracy, precision, recall, and latency
- Monitor for data drift to detect input changes that affect predictions
- Use dashboards and alerts for real-time insights
- Periodically retrain models to adapt to new data patterns
Teams that adhere to these practices can maintain optimal model performance and reliability.
4. What Tools Are Recommended For DevOps-Based ML Deployment?
Several tools simplify machine learning deployment with DevOps:
- CI/CD Platforms: Jenkins, GitLab CI, GitHub Actions
- ML Versioning Tools: MLflow, DVC, or cloud-native platforms like AWS SageMaker and Azure ML
- Monitoring Tools: Prometheus, Grafana, or specialized ML monitoring solutions.
Selecting the right tools ensures a smooth, scalable, and maintainable ML production pipeline.
Conclusion
Deploying machine learning models works best when DevOps practices guide the process. First, testing models in production, tracking performance metrics, and maintaining clear workflows reduces risks such as downtime, data drift, and unexpected errors, keeping models accurate and reliable under real-world conditions.
As a result, teams can confidently update and scale models without disrupting operations.
Additionally, the model type used can significantly impact deployment outcomes. Exploring the Difference between large language models and traditional ML approaches helps align strategies with operational goals and improves overall effectiveness.
In the end, structured pipelines, active monitoring, and well-planned model implementation allow teams to achieve smooth, efficient, and predictable ML deployments.
Concerned about ML models losing accuracy over time or facing unexpected errors?







Share your thoughts about this blog!