Application modernization has shifted from being optional to becoming essential for competitiveness. Moving from legacy systems to cloud-native architectures allows organizations to achieve agility, scalability, and cost efficiency through cloud microservices solutions.
Legacy app modernization aims to upgrade individual applications for better performance and compatibility. However, it is part of a larger effort called legacy software modernization.
This broader effort includes updating the entire software stack, cloud infrastructure for microservices, and integration processes. This transformation enables faster innovation, improved user experiences, and the ability to adapt to market demands quickly.
In this blog, we will explore how microservices architecture on the cloud helps modernize applications. This approach allows organizations to move away from large, monolithic systems. It also helps them become more agile and flexible.
However, let’s first learn what the benefits of application modernization are.
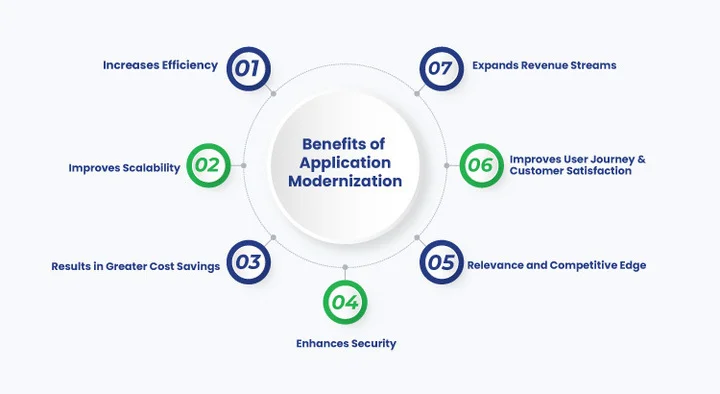
From Monolithic to Microservices Architecture: The Shift to Cloud-Native
One of the most significant shifts in modernization is moving from monolithic architectures to microservices in the cloud. Unlike monoliths, which tightly couple all components, a microservices architecture divides applications into smaller, independent services.
This approach enables service isolation in microservices, allowing teams to develop, deploy, and scale components independently, improving reliability and reducing time-to-market.
Table of Contents
Adoption of cloud-native microservices and modern designs is rapidly growing. CNCF reports that more than 85% of businesses now use microservices for complex applications. Gartner predicts that global cloud spending will hit $1.8 trillion by 2025.
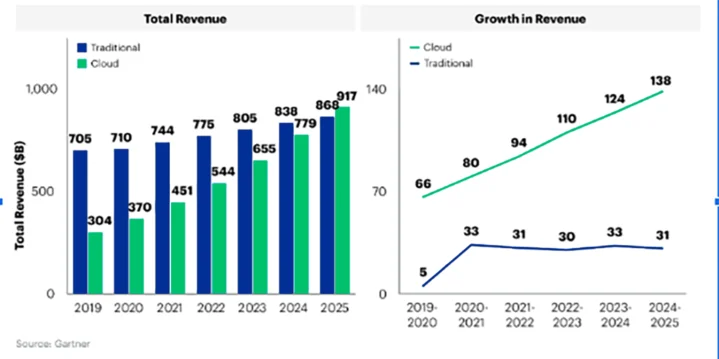
This widespread adoption highlights a clear industry trend: embracing enterprise microservices architecture is a proven path to innovation and operational excellence.
This guide explains how to modernize your applications. It offers a clear guide for moving to a microservices architecture.
This will help you upgrade from old systems. You can build a foundation that is ready for the future. However, let’s first discuss the microservices architecture for a better understanding.
What Is Microservices Architecture?
Microservices architecture is a modern software design solution where applications are built as a collection of small, independent services that work together. Each service focuses on a specific business capability and communicates with others through lightweight APIs or messaging systems. This model supports microservices scalability on cloud platforms and is key to building cloud microservices that are resilient and efficient.
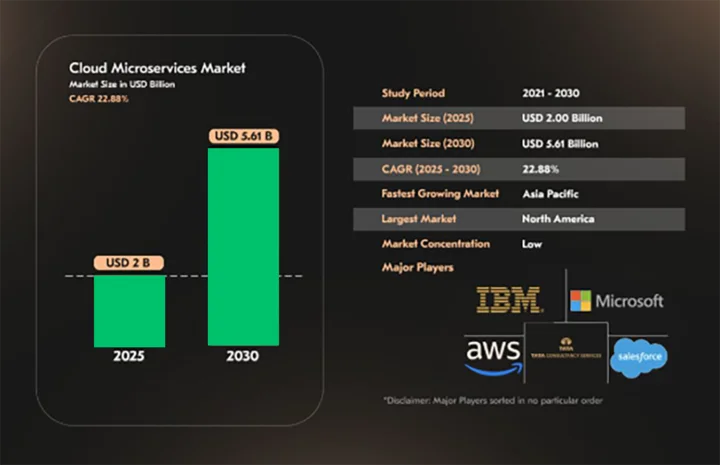
In contrast to traditional monolithic setups, this design supports event-driven microservices architecture, rapid development, and distributed tracing in microservices for better observability. The cloud microservices architecture market is projected to grow from $2 billion in 2025 to $5.61 billion by 2030, highlighting its increasing relevance.
What Is Application Modernization?
Application modernization is the process of transforming existing, often legacy, software applications to align with modern technologies, microservices best practices, and evolving business needs. The goal is to improve agility, scalability, and performance, the core benefits of microservices architecture for scalable cloud apps.
<2>Significant Modernization Shifts: What You Need to Know
Modernization is defined by several shifts that reshape how organizations build and manage applications.
Let’s take a closer look at them.
1. From Monoliths to Microservices Architecture
Traditionally, applications were large, interdependent systems. Modernization replaces these with cloud-native microservices, enhancing agility and reducing operational risk. Companies rely on microservices consulting services to navigate this shift efficiently.
From On-Premise to Cloud-Native
This involves migrating from traditional servers to cloud platforms that support microservices deployment on the cloud. Tools like Kubernetes, containers, and serverless functions power the application modernization trends of 2025 and ensure alignment with CI/CD for microservices architecture.
Why Does Application Modernization Matter?
Modernization is more than an option now. Global spending on modernization is projected to rise from $29.9B in 2024 to $74.6B by 2030.
Core business systems built on legacy COBOL, Java, or .NET still power critical operations but lack the agility for cloud microservices architecture use cases.
Without modernization, these systems cannot work properly. Organizations must understand how the cloud enables microservices transformation to stay innovative and competitive.
Is Your Legacy System Holding You Back From Competing? We can help you break free from rigid monoliths, scale on demand, and deliver applications faster with fewer risks.
Why Microservices Architecture on the Cloud?
Combining microservices architecture with cloud infrastructure brings major advantages in scalability, resilience, and cost-efficiency. Let’s explore how:
1. Scalability
Each service in a cloud-native microservices architecture can scale independently. The cloud’s auto-scaling capabilities are crucial for microservices scalability on the cloud:
- Handle unpredictable traffic.
- Optimize resource use.
- Avoid over-provisioning.
2. Fault Tolerance & Resilience
Secure microservices architecture ensures that failures in one service don’t impact others. Tools like Istio and Kubernetes support self-healing containers and automatic failover.
3. Agile & Continuous Development
Implementing microservices with CI/CD pipelines allows independent updates without downtime. This supports blue-green deployments, automated testing, and microservices observability and monitoring best practices.
Popular tools include GitHub Actions, AWS CodePipeline, and Helm.
4. Cost Efficiency
Cost efficiency plays an important role in ensuring that resources are maximized while minimizing unnecessary expenses.
The cloud supports:
- Pay-as-you-go billing
- Serverless scaling (e.g., AWS Fargate)
- Minimal infrastructure overhead
A Step-by-Step Microservices Architecture Guide for Modernization
Modernizing legacy systems into cloud microservices solutions requires careful planning, strategic execution, and iterative improvement. This step-by-step guide helps organizations effectively shift to a cloud-native microservices model, enabling scalability, agility, and future-readiness.
1. Analyze Your Applications
Begin with a comprehensive audit of your application portfolio. Catalog each application, its purpose, current usage, technical stack, dependencies, and user base. This assessment should also evaluate infrastructure needs, security gaps, and scalability limitations.
- Identify components that can be broken down into microservices design patterns.
- Evaluate integration complexity and legacy bottlenecks.
- Consider which applications are suited for microservices scalability on cloud platforms.
- Understanding these aspects early helps determine the feasibility and the scope of application modernization.
2. Identify Business Goals
Modernization must be driven by business objectives, not just technical convenience. Clarify the business outcomes you aim to achieve, such as:
- Faster time-to-market
- Enhanced user experience
- Improved operational efficiency
- Lower maintenance costs
- Better compliance and security
Aligning IT modernization efforts with these goals ensures measurable success. A robust microservices architecture for scalable cloud apps should directly support your digital transformation strategy.
3. Choose a Modernization Path
Not all legacy systems need the same level of transformation. Based on the business and technical evaluation, decide on the most appropriate path for each application:
- Rehost: “Lift and shift” to the cloud with minimal code changes.
- Refactor: Optimize existing code to align with cloud-native microservices capabilities and platform efficiencies.
- Rearchitect: Restructure applications by applying microservices design patterns to improve scalability, performance, and maintainability.
- Rebuild or Replace: Build from scratch or replace legacy apps with off-the-shelf or custom microservices-based solutions.
This decision-making process forms the foundation of your microservices migration strategies for enterprises, especially in highly regulated or mission-critical environments.
4. Set Priorities
With goals and strategies in place, prioritize applications based on their business value, complexity, and risk:
- Start with “low-hanging fruit” applications that are high-impact but lower in complexity.
- Use CI/CD for microservices architecture to accelerate initial phases.
- Gradually scale to more complex systems once early wins validate the strategy.
This phased approach builds momentum and confidence across stakeholders.
5. Build a Roadmap
A well-defined roadmap is key to a successful transformation. It should include:
- Short-term and long-term modernization goals
- A timeline for each application’s journey
- Required skill sets and external support (e.g., microservices consulting services)
- Budgets, risks, and contingency planning
This roadmap must be realistic, flexible, and based on cloud application modernization services best practices. Collaboration across teams, engineering, DevOps, and business is essential.
6. Execute the Plan
Execution involves transforming strategy into action. At this stage:
- Begin coding, containerizing, and integrating services into cloud infrastructure for microservices.
- Adopt microservices and container orchestration platforms like Kubernetes for deployment and scalability.
- Ensure all services comply with secure microservices architecture standards.
- Partner with a microservices development company to streamline execution and reduce risk.
- Use API gateways to manage traffic efficiently, following microservices API gateway best practices.
Training internal teams is critical; modernization is as much about people and culture as it is about code.
7. Monitoring
Post-deployment, continual monitoring is crucial. Establish metrics aligned with your business objectives and utilize microservices observability and monitoring best practice tools, such as:
- Distributed tracing in microservices for pinpointing bottlenecks
- Logging and metrics dashboards for service-level performance
- Real-time feedback loops from users and teams
This helps ensure your systems perform as expected in live cloud environments and allows proactive issue resolution.
8. Continuous Improvement
Application modernization is an ongoing journey, not a one-time event. Use feedback, analytics, and performance reviews to refine services:
Revisit your microservices architecture regularly for optimization opportunities.
- Automate improvements using CI/CD pipelines for deployments.
- Implement an event-driven microservices architecture to handle dynamic business logic and real-time data.
- Apply lessons learned to future modernization initiatives to improve speed, reduce cost, and avoid repeated pitfalls.
Adopting a culture of continuous improvement ensures your systems remain competitive, efficient, and aligned with the latest application modernization trends for 2025.
Struggling To Scale without rising costs or complexity?
What are Common Cloud Migration Challenges?
Cloud migration brings agility and scalability, but this journey is often met with challenges such as increased cost, security risks, and operational complexity. So, despite the benefits, migrating to cloud-native microservices isn’t easy:
1. Lack of Migration Strategy
Jumping into cloud adoption without a roadmap often leads to disruption. Workloads must be evaluated carefully to decide what belongs in the cloud versus on-premises.
Solution: Define clear goals, assign responsibilities, and map dependencies. Use automation and choose between public, private, or hybrid cloud based on business needs.
2. High Migration Costs
Expenses are often underestimated, from bandwidth demands to ongoing cloud usage fees.
Solution: Use planning tools, set realistic budgets, and account for both migration and post-migration costs.
3. Complex Architecture
Legacy IT systems can make alignment with cloud strategies difficult, leading to interoperability issues.
Solution: Use an enterprise microservices architecture to gradually modernize.
4. Security & Compliance Risks
Data transfers expose sensitive information to potential threats. Cloud systems must meet the same or stronger security standards as on-premises environments.
Solution: Select providers with strong security records, use private connections for sensitive data, and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements to ensure a secure microservices architecture with compliance tools and private data connections.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What Are The Best Tools For Microservices Deployment On The Cloud?
Popular tools for deploying microservices on the cloud include:
- Kubernetes (EKS, GKE, AKS) for container orchestration
- Docker for containerization
- AWS Lambda and Azure Functions for serverless deployments
- Istio for service mesh and traffic management
These tools streamline the deployment, scaling, and monitoring of microservices in cloud environments.
What Are The Benefits Of Microservices In Cloud Environments?
Common benefits of microservices in a cloud environment include:
- Scalability: Each service can scale independently.
- Agility: Faster development and deployment cycles.
- Resilience: Failures in one service don’t disrupt the entire system.
- Cost-efficiency: Improved resource allocation in the cloud.
- Flexibility: Easy integration with cloud-native services and APIs.
What Are The Common Microservices Migration Strategies For Enterprises?
- Strangler Pattern: Gradually replace legacy features with microservices.
- Re-platforming: Moving applications to containers or serverless frameworks.
- Re-architecting: Redesigning applications to fully adopt cloud-native microservices.
- Incremental Migration: Shifting components in phases while keeping the system operational.
What Are The Cloud Microservices Architecture Use Cases?
- eCommerce Platforms: Independent services for catalog, payment, and user accounts.
- Banking & Fintech: Secure and scalable services for transactions and fraud detection.
- Healthcare: Modular systems for patient records, billing, and telemedicine.
- Streaming Services: Media delivery, recommendations, and subscriptions handled separately.
- IoT Applications: Real-time data collection, processing, and analytics through microservices.
Conclusion
Microservices architecture on the cloud is essential for agility, speed, and innovation. The move from monoliths to cloud-native microservices is a proven strategy for resilience and growth.
Cloud migration is more than a technology shift. It focuses on modernization and aligning IT with business goals. For those wondering about how to modernize legacy applications with microservices, the time to act is now.
Clustox helps organizations modernize applications with efficiency and strategy. Our Consulting Services Include:
- Assessment & Strategy: Developing clear modernization roadmaps for your business goals.
- Microservices Development: Building scalable, cloud-ready solutions designed for flexibility.
- Cloud Migration: Utilizing expertise in AWS to ensure smooth transitions.
- DevOps & CI/CD: Enabling continuous delivery with best practices in a microservices API gateway.
We focus on secure, reliable deployment of microservices in the cloud with full support for container orchestration platforms. Together, we can build a future-ready microservices architecture that fits your organizational goals.
Want to achieve continuous delivery, faster innovation, and improved user experiences without disrupting operations?






Fantastic guide! This article breaks down microservices architecture on the cloud step by step, making application modernization much easier to grasp. Very insightful for developers and IT teams aiming to build scalable, efficient systems.