IT operations are advancing rapidly to meet demands for speed, agility, and automation, areas where traditional models often fall short. To address this, organizations are adopting DevOps and AIOps, two approaches with distinct methods but a shared goal of improving efficiency.
DevOps simplifies software delivery by unifying development and operations through collaboration, automation, and CI/CD, enabling faster releases and stable systems. AIOps, meanwhile, utilizes modern AI driven solutions to analyze large datasets, detect anomalies, and automate responses, adding predictive intelligence to IT operations.
Rather than choosing between them, businesses gain the most by combining DevOps’ collaborative automation with AIOps’ intelligent insights. The right balance depends on organizational goals.
So, which strategy is better suited to your organization’s goals: DevOps, AIOps, or a hybrid of both?
In this article, we’ll examine their core differences and practical use cases.
What is DevOps?
DevOps is a modern software development methodology that focuses on unifying development and IT operations teams. According to Market and Market research, the DevOps market share is expected to reach $25.5 billion by 2028 at a CAGR of 19.7% from 2023 to 2028.
By promoting a culture of collaboration, automation, and iterative improvement, DevOps enables organizations to accelerate software delivery and improve application quality.
Better communication between these traditionally separate teams minimizes errors and ensures reliable deployment cycles. AI in DevOps is now playing an important role by increasing automation, enabling predictive insights, and improving operational efficiency across the software lifecycle.
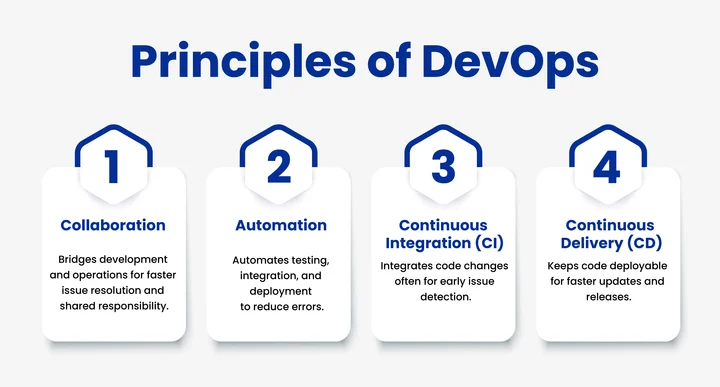
Principles of DevOps
DevOps is more than just a set of practices; it bridges the gap between development and operations, delivering software faster, more reliably, and with greater collaboration. By embracing its core principles, organizations can simplify workflows, improve efficiency, and increase customer satisfaction.
Table of Contents
Below, we’ll explore the key principles of DevOps, highlighting how each contributes to building a culture of automation, continuous improvement, and shared responsibility.
Key Advantages of DevOps
Organizations adopting DevOps gain several advantages that enhance their software development life cycle (SDLC), often with the support of experienced software development partners.
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Accelerated Delivery | Automation and tighter coordination between teams speed up the development-to-deployment pipeline. |
| Teamwork | Encourages real-time communication and shared goals, reducing misunderstandings and project delays |
| Increased Efficiency | Automated workflows and consistent monitoring eliminate repetitive tasks and optimize performance |
| Lower Risk of Downtime | Early identification and resolution of coding issues help prevent failures during production |
Popular DevOps Tools Comparison
DevOps relies on various tools to support its automation and collaboration goals. DevOps tooling includes:
- Jenkins: A powerful open-source automation server used for building and testing software projects continuously.
- Kubernetes: Automates deployment, scaling, and operation of application containers across clusters of hosts.
- Docker: Simplifies the process of packaging, deploying, and running applications in isolated environments.
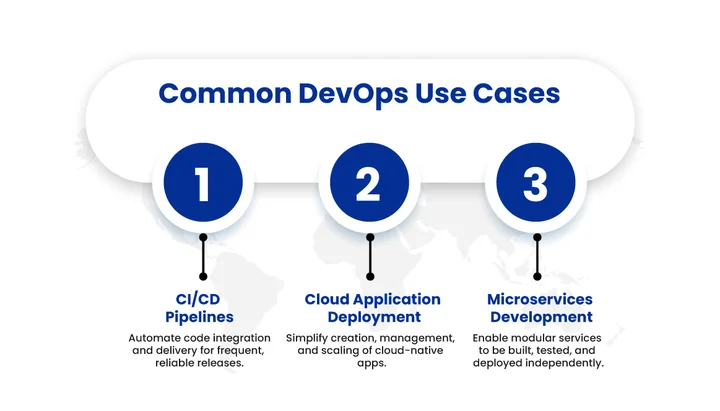
DevOps Use Cases
DevOps is not a one-size-fits-all approach; it adapts to different industries and business needs by enabling faster delivery, improved collaboration, and increased reliability. From accelerating software releases to strengthening security, its applications extend across various domains.
Below are the practical scenarios where DevOps brings measurable value, highlighting how it transforms traditional processes into agile, efficient, and scalable operations.
Facing IT complexity and downtime despite DevOps? Improve reliability and efficiency with expert-driven strategies.
What is AIOps?
AIOps, short for Artificial Intelligence for IT Operations, introduces AI and machine learning to traditional IT management. Its primary goal is to manage the complexity of modern IT environments by processing and analyzing large volumes of data. According to Mordor Intelligence, the AIOps market was valued at USD 16.42 billion in 2025 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 17.39%, reaching USD 36.60 billion by 2030.
AIOps platforms help detect anomalies, predict failures, and provide insights for optimizing system performance before issues impact users.
How Does AIOps Function?
AIOps platforms gather data from multiple sources such as logs, metrics, and traces. This data is then processed using machine learning algorithms to uncover patterns, forecast potential disruptions, and automate remediation tasks, showcasing the growing impact of AI in IT operations to improve efficiency and responsiveness.
Principles of AIOps
AIOps brings machine learning and big data together to make IT systems smarter, faster, and more proactive. Instead of relying on manual monitoring and reactive fixes, AIOps enables organizations to predict issues, automate responses, and uncover insights from massive volumes of operational data.
Below are the fundamental principles that guide AIOps, showing how they help enterprises achieve resilience, efficiency, and intelligent decision-making in complex digital environments.

Key Benefits of AIOps
Here are some impactful benefits that AIOps brings to IT operations:
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Early Issue Detection | Identifies system irregularities early, reducing the time to resolution and preventing disruptions |
| Efficient Incident Response | Automates event management and alert correlation to resolve issues faster |
| Data-Driven Insights | Transforms raw data into actionable intelligence, helping IT teams make better strategic decisions |
Top AIOps Tools
Leading AIOps platforms include:
- Splunk: Uses AI to monitor, analyze, and visualize machine data for better decision-making and issue tracking.
- Dynatrace: Offers AI-powered monitoring and observability to detect performance bottlenecks and user-impacting issues.
- Moogsoft: Focuses on event correlation and noise reduction, helping teams resolve problems with greater speed and precision.
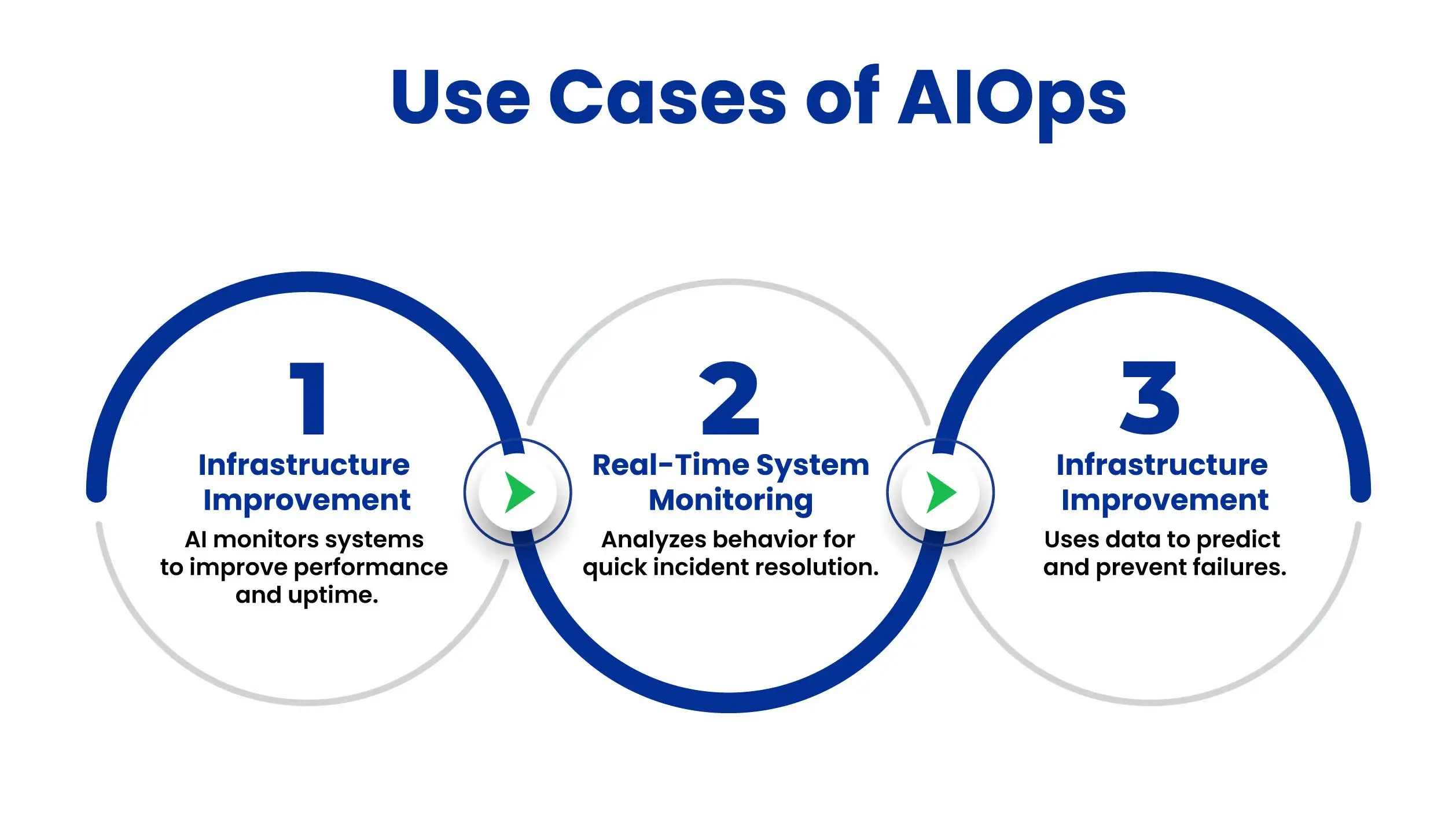
AIOps Use Cases
The value of AIOps becomes most evident when applied to real-world IT challenges. By combining automation, analytics, and machine learning, AIOps helps organizations manage complex systems with greater precision and speed. From reducing downtime and improving incident response to increasing resource utilization, its impact can be seen across diverse IT operations.
Let’s explore practical scenarios where AIOps delivers measurable results, demonstrating how it transforms traditional operations into intelligent, adaptive, and future-ready ecosystems.
Tired of reactive issue handling and inefficient incident resolution cycles? Let us help you implement intelligent monitoring and predictive analytics with AIOps.
What are the Differences Between DevOps and AIOps?
DevOps and AIOps serve distinct but complementary roles in modern IT environments. Here’s a breakdown of how they differ across key aspects:
1. Core Objective
DevOps focuses on enhancing the speed and reliability of software delivery by promoting collaboration between development and operations teams. Its main goal is to eliminate silos, streamline workflows, and minimize deployment errors.
AIOps, on the other hand, introduces artificial intelligence and machine learning to automate IT operations. It aims to manage system complexity and improve performance through intelligent data analysis and real-time insights.
2. Role of Automation
DevOps employs automation for standard development tasks like code integration, testing, and deployment (CI/CD). The focus is on reducing manual effort and ensuring consistency across development stages.
AIOps takes automation further by using AI-driven algorithms to perform predictive analytics, correlate events, and automate incident detection and resolution, often before human intervention is needed.
3. Handling of Data
In DevOps, data collection primarily revolves around logs, metrics, and system events. These are interpreted manually or with the help of monitoring tools to assess performance and troubleshoot issues.
AIOps uses a broader, more advanced approach. It processes vast volumes of structured and unstructured data across multiple sources using AI/ML models. This enables rapid anomaly detection, pattern recognition, and decision-making without human dependency.
4. Problem Response Strategy
DevOps is largely reactive. Teams respond to incidents as they occur, relying on monitoring tools and alerts to trigger investigations and remediation efforts.
AIOps promotes a proactive approach by anticipating potential failures using historical data trends and predictive analytics. It identifies vulnerabilities before they escalate into real problems.
A Comprehensive Tool Comparison of AIOps & DevOps
The comprehensive tool comparison of AIOps and DevOps reveals how these two approaches utilize distinct capabilities to improve IT operations, simplify workflows, and strengthen system resilience.
| Category | DevOps Tools | AIOps Tools |
|---|---|---|
| Automation | Jenkins: Automates CI/CD pipelines | Moogsoft: Automates incident detection and correlation |
| Configuration | Ansible, Terraform: Infrastructure as code | BigPanda: Automates root cause analysis and event enrichment |
| Containerization | Docker and Kubernetes: Build and manage containers at scale | Dynatrace: Auto-discovers dependencies and anomalies in containerized apps |
| Monitoring | Prometheus, Grafana: Infrastructure and application monitoring | IBM Watson AIOps: Uses ML to detect patterns and reduce alert fatigue |
| Collaboration | GitLab, Bitbucket: Version control and team collaboration | Splunk AIOps: Unifies data sources to aid collaboration and insights |
| Logging & Analysis | ELK Stack: Centralized log management | New Relic Applied Intelligence: AI-powered observability and anomaly detection |
| Incident Management | PagerDuty, Opsgenie: Alerting and on-call scheduling | ServiceNow ITOM: AI-driven service mapping and proactive incident response |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
2. Who Provides the Best AIOps in Networking?
The best provider depends on your network infrastructure, use case, and integration needs. It's advisable to evaluate based on scalability and data correlation capabilities.
3. Are AIOps and DevOps the Same?
No, AIOps and DevOps are distinct but complementary. DevOps focuses on collaboration, automation, and continuous delivery between development and operations teams. AIOps, on the other hand, uses AI/ML to analyze IT operations data, enabling faster incident detection and resolution. AIOps enhances DevOps by adding intelligence to operational processes.
4. Is DevOps Going to Replace AIOps?
DevOps isn't being replaced by AIOps, but it is evolving with it. AIOps enhances DevOps by automating complex operational tasks and providing real-time insights, making DevOps practices more efficient. Many organizations are adopting both to achieve smarter, faster, and more resilient IT operations.
Conclusion
AIOps and DevOps address different aspects of modern IT and software development workflows, yet they can work in tandem to deliver more resilient, scalable, and efficient systems. While DevOps focuses on enhancing collaboration, accelerating deployment, and reducing manual errors, AIOps brings intelligent automation and real-time decision-making to IT operations through AI and machine learning.
To truly understand AIOps vs. DevOps, it is essential to learn the key differences, use cases, and toolsets for each to help organizations adopt the right combination for their needs. Organizations aiming to adopt To build a more resilient and adaptive IT infrastructure, organizations must hire DevOps experts. Partnering with the right experts ensures smooth integration of automation, observability, and AI, building a solid foundation for scalable, intelligent operations.
Dealing with Constant Deployment Delays and Misaligned Workflows?






Excellent article! This guide clearly explains the key differences between AIOps and DevOps, their use cases, and tool comparisons, making it easier for IT professionals to choose the right approach in 2025. Very informative and practical!