Have you ever wondered how your health information travels safely between apps, hospitals, and clinics?
Healthcare APIs make this possible by acting as bridges that connect disparate systems and ensure patient data flows smoothly. But with greater connectivity comes great responsibility.
A recent study found that 84.7% of healthcare organizations experienced an API security incident in the past year, underscoring the importance of securing this data.
These APIs improve patient care, reduce delays, and help healthcare providers make faster, more informed decisions.
In this blog, we will explore the essential standards, security considerations, and API security best practices for healthcare API integration.
So let’s begin by looking at the essential standards!
What are the Essential Standards for Healthcare API Integration?
Healthcare systems rely on standardized protocols to exchange information accurately and securely. These standards play a significant role in digital transformation services in healthcare by ensuring that patient data flows consistently between applications, thereby enhancing operational efficiency and the quality of care.
Integration of APIs requires adherence to these essential standards, which help developers and healthcare organizations implement interoperable and compliant solutions.
In the following, we will discuss the most widely adopted standards that underpin interoperability in healthcare:
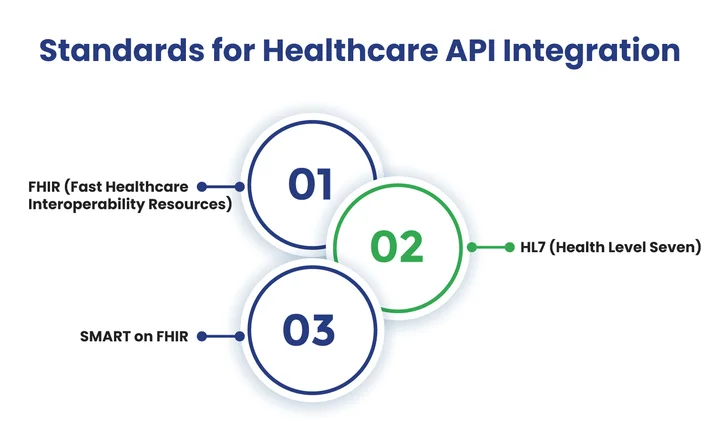
Table of Contents
1. FHIR (Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources)
FHIR is a modern standard designed to simplify the exchange of healthcare information through APIs. It represents clinical data as modular “resources,” such as patients, medications, or appointments.
Developers can create interoperable apps that safely exchange current, accurate patient data between healthcare systems using the FHIR API.
2. HL7 (Health Level Seven)
HL7 integration is a foundational standard for healthcare data exchange. It defines the structure and format for electronic health records, lab results, and other clinical information.
APIs that adhere to HL7 ensure that different healthcare systems communicate consistently, reducing errors and improving the efficiency of patient care.
3. SMART on FHIR
SMART on FHIR is an extension of the FHIR API standard that adds a framework for secure, standardized app integration. It allows third-party applications to access healthcare data securely while maintaining patient privacy.
With SMART on FHIR, developers can create interoperable apps that seamlessly integrate with existing healthcare systems, improving functionality and the user experience.
Keep reading to know about the security considerations.
Build secure and HIPAA-compliant APIs that power encrypted data exchange and deliver better patient outcomes.
What Security Considerations Should Healthcare APIs Follow?
Healthcare APIs handle highly sensitive patient information, making security a critical concern. It ensures that data is protected during transmission and storage.
This is essential not only for compliance with regulations such as HIPAA but also for maintaining patient trust and the integrity of healthcare systems.
When designing and integrating healthcare APIs, organizations must carefully consider multiple security aspects to prevent unauthorized access, data breaches, and other risks.
Let’s explore the essential security considerations healthcare API integrations should follow to safeguard patient data effectively:
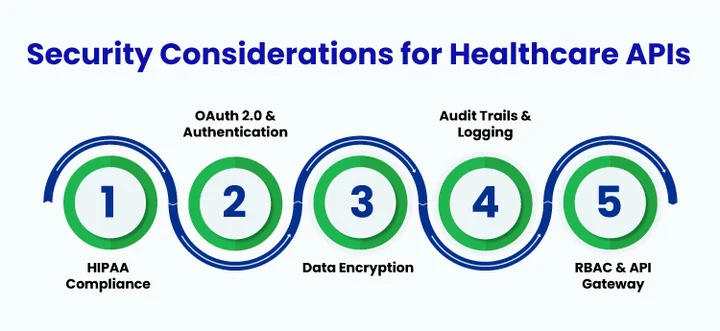
1. HIPAA Compliance
APIs must adhere to HIPAA regulations to protect patient health information. This includes implementing safeguards for privacy and security, breach notifications, and ensuring that sensitive data is handled in accordance with legal standards.
2. OAuth 2.0 and Authentication
Secure authentication is essential to control who can access the API. OAuth 2.0 in healthcare verifies user identities and manages permissions, preventing unauthorized access to sensitive healthcare data.
3. Data Encryption and Secure Transmission
All data exchanged through APIs should be encrypted both in transit and at rest. Protocols such as TLS for transmission and AES for storage ensure that patient information remains protected from interception or theft.
4. Audit Trails and Logging
Maintaining detailed logs of API activity allows healthcare organizations to monitor access, detect suspicious behavior, and demonstrate compliance. Audit trails are critical for accountability and incident response.
5. Input Validation and Threat Protection
APIs must validate incoming data to prevent attacks such as SQL injection, XSS, and other exploits. Strict input validation and security checks ensure the system processes only safe and expected information.
6. Regular Security Testing and Updates
Frequent vulnerability assessments, penetration testing, and timely software updates are necessary to address security weaknesses. Regular maintenance reduces the risk of exploitation by attackers.
7. Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
Implementing RBAC ensures that users can only access data relevant to their roles. This limits unnecessary exposure of sensitive information and strengthens overall system security.
8. Secure API Gateway and Rate Limiting
Using an API gateway helps manage traffic, enforce security policies, and prevent abuse. Rate limiting and throttling reduce the risk of denial-of-service (DoS) attacks and help maintain API stability.
With the security foundations in place, the next step is understanding how to put them into practice for reliable API integration.
Which Best Practices Should Organizations Follow for Healthcare API Integration?
Integrating healthcare APIs effectively requires more careful planning, security, and adherence to standards. Following best practices ensures that patient data is exchanged accurately, securely, and in a way that supports seamless interoperability between healthcare applications.
This approach not only protects sensitive information but also improves operational efficiency and overall care quality.
As the healthcare software development industry continues to evolve around these principles, it is essential to ensure that digital health solutions remain secure, compliant, and interoperable across platforms.
Here are proven best practices for securely, efficiently, and reliably integrating healthcare APIs:
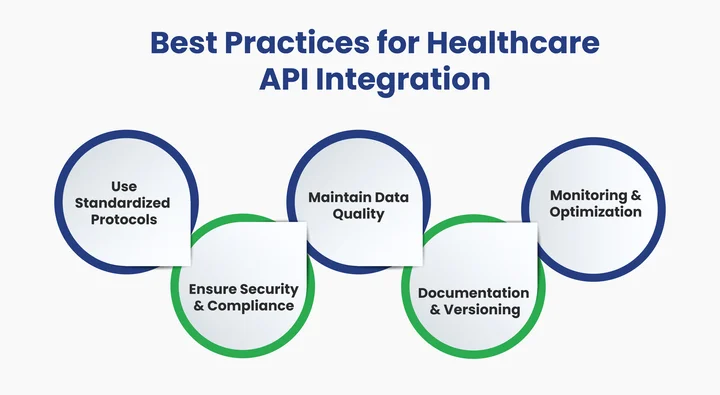
1. Use Standardized Protocols
Adhering to widely accepted standards like FHIR, HL7, and SMART on FHIR ensures that healthcare APIs can communicate effectively across different systems. Standardized protocols reduce integration errors, improve interoperability, and make it easier for developers to maintain and scale applications.
2. Ensure Security and Compliance
Healthcare APIs handle sensitive patient data, so security cannot be compromised. Implement strong authentication and authorization protocols, encrypt data in transit and at rest, and comply with regulations like HIPAA. A secure API protects both patient privacy and organizational reputation.
3. Maintain Data Quality and Consistency
Accurate and consistent data are crucial for clinical decision-making. Validate all incoming and outgoing data, handle errors gracefully, and implement mechanisms to prevent duplication or loss. Reliable data ensures better patient outcomes and smoother operations.
4. Provide Clear Documentation and Versioning
Well-documented APIs reduce integration time and prevent misunderstandings. Include usage guidelines, example requests and responses, and clearly define versioning practices. Proper documentation helps both internal teams and third-party developers work efficiently.
5. Monitor, Test, and Optimize
Continuous monitoring of API performance, coupled with regular testing, helps identify bottlenecks, security vulnerabilities, and potential failures before they impact users. Use logging, automated tests, and performance metrics to optimize APIs for reliability and scalability.
6. Implement Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
Limit data access according to user roles to prevent unnecessary exposure of sensitive information. RBAC ensures that only authorized personnel can access specific functions and datasets, strengthening overall security.
7. Use API Gateways and Throttling
An API gateway can manage traffic, enforce security policies, and prevent abuse. Throttling and rate limiting protect APIs from overload or denial-of-service attacks while maintaining service stability.
Healthcare companies can create secure, dependable, and interoperable APIs by adhering to these best practices, which will ultimately improve patient care and operational efficiency.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
2. Why is HIPAA Compliance Critical for Healthcare APIs?
HIPAA compliance ensures that healthcare APIs follow strict privacy and security standards for patient data. Non-compliance can lead to serious breaches, heavy fines, and reputational damage. Healthcare organizations can safely store, transfer, and handle patient data while upholding public confidence by adhering to HIPAA regulations.
3. How Does OAuth 2.0 Benefit API Security in Healthcare?
OAuth 2.0 allows healthcare systems to grant controlled access to data without sharing passwords. It verifies user identities, limits permissions, and prevents unauthorized access to protected health information (PHI), making it a cornerstone of secure healthcare API design.
4. What Are the Best Practices for Securing Healthcare API Data?
To strengthen the security of healthcare APIs, organizations should:
- Encrypt all data in transit (TLS) and at rest (AES).
- Implement Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) to restrict data exposure.
- Use API gateways for traffic monitoring and policy enforcement.
- Conduct regular security testing and penetration assessments.
- Apply input validation to block malicious requests and prevent injection attacks.
- Keep systems up to date with the latest patches and security fixes.
5. How Can Healthcare Organizations Improve Interoperability Using APIs?
To achieve seamless data sharing and better interoperability, healthcare organizations should:
- Adopt standardized protocols like FHIR, HL7, and SMART on FHIR.
- Ensure consistent data formatting across applications and systems.
- Use secure API gateways to manage traffic and enforce compliance policies.
- Validate data accuracy to prevent duplication or mismatches.
- Collaborate with trusted development partners who specialize in healthcare API integration and compliance.
Final Takeaway: Ensuring Secure and Compliant Healthcare API Integration
As healthcare systems become more connected, ensuring that patient data flows securely between apps and providers is a significant responsibility. Without proper standards, security, and integration practices, organizations risk data breaches, compliance issues, and loss of patient trust.
How can healthcare providers effectively overcome these challenges?
Partnering with Expert backend development services offers a reliable solution. Skilled developers implement secure authentication using OAuth 2.0 in healthcare, strong healthcare data encryption, and role-based access controls while maintaining smooth interoperability in healthcare.
This approach transforms complex healthcare data flows into compliant, efficient, and dependable APIs, allowing providers to focus on delivering high-quality patient care.
Want to turn complex healthcare data into intuitive and secure systems?







Share your thoughts about this blog!