Have you ever wondered how your phone seems to know which app to suggest next, or how streaming services always recommend shows you might like?
Behind the scenes, AI agents are making this possible. They observe, learn, and act autonomously to make daily tasks easier and more efficient.
AI agents help us manage schedules, suggest content, and even control smart devices, adapting to our habits and preferences. Businesses are using them to improve customer experiences, automate repetitive tasks, and make faster decisions.
The global AI agents market is growing rapidly. A recent PR Newswire report estimates that the global AI agents market will jump from USD 5.32 billion in 2025 to USD 42.7 billion by 2030, achieving a strong 41.5% CAGR.
This growth highlights how rapidly industries are adopting AI solutions. This growth shows just how important AI-driven solutions are becoming across industries.
This rapid expansion reflects the growing demand for automation and personalized experiences. As businesses and individuals seek smarter, more efficient ways to operate, AI agents are becoming integral to daily life, enhancing productivity and user satisfaction.
In this blog, we will explore the definition of AI agents, look into their various types, and examine real-world use cases to understand their impact and potential.
What are AI Agents?
AI agents are intelligent systems that observe their environment, make decisions, and take actions autonomously to achieve specific goals. Unlike traditional software, they can adapt, learn from experience, and improve over time.
Table of Contents
These agents power everyday technology, from virtual assistants and recommendation engines to smart home devices and self-driving cars. By combining perception, reasoning, and action, AI agents help users and businesses complete tasks more efficiently and intelligently.
How Do AI Agents Work?
AI agents interact with their environment to perceive changes, make decisions, and take actions automatically. Unlike traditional software, they can learn from experience and adjust their behavior over time.
At a high level, AI agents follow a continuous cycle of perception, reasoning, and action:
Here’s a breakdown of the key steps in how AI agents operate:
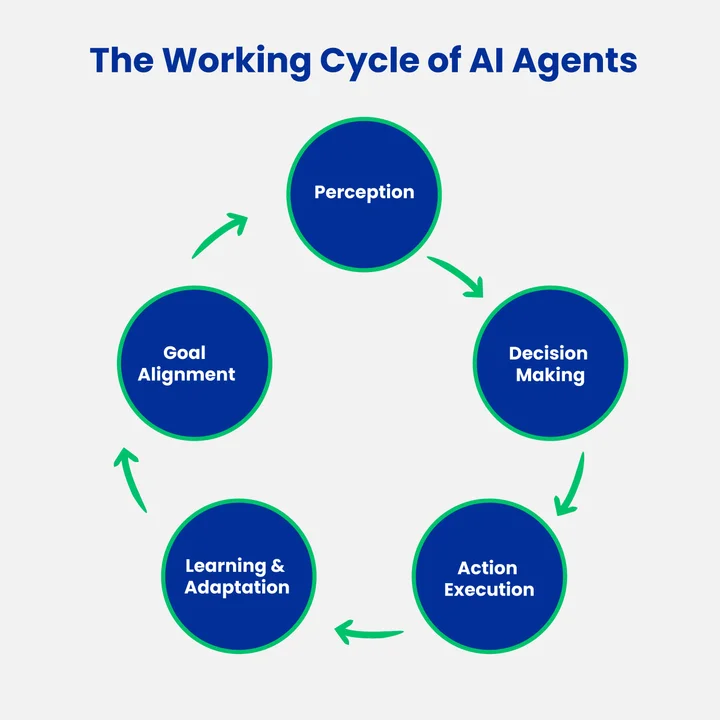
- Perception: They gather information from sensors, data inputs, or digital feeds to understand their surroundings. This could be tracking user behavior on a website or monitoring real-world conditions in a factory.
- Decision Making: Once the environment is understood, the agent evaluates possible actions using rules, algorithms, or machine learning models to pick the best one.
- Action Execution: After deciding, the agent performs the action. This might involve sending a notification, adjusting a process, or interacting with another system.
- Learning and Adaptation: Many AI agents learn from past outcomes to make better decisions in the future. With advanced Agentic AI development, these agents don’t just repeat predefined actions. They adapt to changing environments, improve continuously, and handle new challenges more effectively.
- Goal Alignment: They continually check whether their actions are helping achieve objectives and adjust strategies if needed.
This process allows AI agents to work independently while staying aligned with user or business goals. It’s this combination of perception, reasoning, and action that makes them more intelligent and versatile than traditional automated systems.
Cut repetitive tasks & costs by up to 30% with AI agents and see immediate wins for your team.
What Are the Different Types of AI Agents, and How Do They Work in 2026?
In 2026, AI agents differ in how they perceive their environment, make decisions, and take actions. Some respond instantly to changes, while others plan to achieve specific goals. Knowing these kinds enables us to comprehend how AI agents work in practical applications, such as self-driving cars and virtual assistants.
Different types of AI agents are designed to suit different tasks, making them more effective in achieving objectives and improving user experiences.
Let’s discuss the main types of AI agents and see how each one operates in practice:

1. Simple Reflex Agents
Simple reflex agents are the most basic type of AI agent. They react directly to the current situation using predefined rules, without considering past experiences or future consequences. Think of them as “if this happens, do that” systems.
How They Work:
These agents sense the environment, check it against a set of rules, and perform the corresponding action immediately. They don’t plan or store information about previous states; they just respond to what they see now.
Why It Matters:
Simple reflex agents are fast and efficient for straightforward tasks where conditions are predictable. However, they struggle in dynamic environments where planning or memory is required.
Example In Real Life:
Smart-home IoT devices like basic motion-sensor lights or simple thermostats work this way. They detect a change (motion or temperature) and trigger an action instantly (turn lights on, adjust temperature) without remembering past events.
2. Model-Based Reflex Agents
Unlike simple reflex agents, model-based reflex agents keep track of the environment. They use a model of the world to understand past states and predict future ones. This allows them to make smarter decisions in more complex situations.
How They Work:
These agents maintain an internal representation of the environment. When they sense something, they update their model and choose actions based on both the current situation and what they know about past events.
Why It Matters:
Model-based agents are more adaptable than simple reflex agents. They work well in dynamic environments where past information influences decision-making, making them suitable for tasks like robotics, navigation, and complex automation.
Example In Real Life:
Autonomous robots in warehouses (like Amazon’s Kiva robots) use a model of their surroundings to track inventory locations and other moving robots. They can navigate safely and efficiently instead of just reacting to one sensor input at a time by maintaining this internal map.
3. Goal-Based Agents
Goal-based agents are smarter than reflex-based agents because they make decisions to achieve specific objectives rather than just reacting to the current situation. They evaluate different possible actions and choose the ones that help them reach their goals.
How They Work:
These agents consider the future consequences of their actions. They plan a sequence of steps that will move them closer to their goal, often weighing multiple options before acting.
Why It Matters:
Goal-based agents are ideal for tasks where planning is required. They excel in environments that need reasoning and strategic decision-making, from gaming and robotics to complex business automation.
Example In Real Life:
Self-driving cars are a classic example. They plan entire routes, decide lane changes, and adjust speed to reach a destination safely and efficiently, all while considering multiple factors like traffic, signals, and road conditions.
4. Utility-Based Agents
Utility-based agents go a step beyond goal-based agents. Instead of just aiming to achieve a goal, they evaluate how “good” each possible action is and choose the one that maximizes overall benefit or satisfaction.
How They Work:
These agents assign a utility value to different outcomes and pick actions that lead to the highest utility. This allows them to make more nuanced decisions, especially in situations where there are multiple ways to achieve a goal with varying results.
Why It Matters:
Utility-based agents are powerful in complex scenarios where simply achieving a goal isn’t enough. They aim for the best possible outcome, making them valuable in personalized services, optimization problems, and AI decision-making systems.
Example In Real Life:
An eCommerce recommendation system is a good example. It doesn’t just suggest products randomly; it considers user preferences, past behavior, and potential satisfaction to recommend items most likely to interest the user.
5. Learning Agents
Learning agents are the most advanced type of artificial intelligence agents. They improve their performance over time by learning from experience, feedback, and data rather than relying solely on predefined rules.
How They Work:
These agents have a learning component that allows them to adjust their behavior based on past successes and mistakes. They combine knowledge about the environment with feedback to make better decisions in the future.
Why It Matters:
Learning agents are ideal for dynamic and unpredictable environments. They adapt to changes, handle new situations, and improve over time, making them essential in modern AI applications such as recommendation systems, autonomous vehicles, and adaptive robotics.
Example In Real Life:
Recommendation systems on platforms like Netflix, Spotify, or Amazon are learning agents. They track user preferences, past interactions, and feedback to continuously improve suggestions, making each user’s experience more personalized and relevant over time.
In simple words, Different AI agents handle tasks in their own ways. Using the right type of IoT systems makes life easier because they can help your home comfortable, recommend products you’ll enjoy, or even drive a car safely.
So far, we’ve provided a general overview of each AI agent type along with a brief real-world example. Next, we will take a closer look at them in more detail, exploring how they operate in specific industries and practical applications in 2026.
What Are Some Real-World Use Cases of AI Agents in Daily Life?
Have you ever wondered how your virtual assistant seems to anticipate your needs or how Netflix always recommends the perfect show?
AI agents are working behind the scenes in ways you interact with every day, often without even realizing it. These intelligent systems are designed to observe, learn, and take action to make your life easier and more efficient.
Some of the notable use cases of AI agents include:
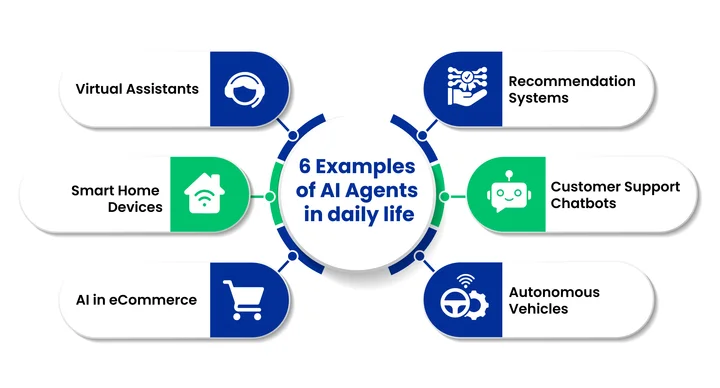
1. Virtual Assistants
Virtual assistants like Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant have become part of our daily routines, often without us even noticing. They can answer questions, set reminders, send messages, or even control smart home devices just by listening to your voice. Imagine waking up in the morning and asking your assistant for the weather, your schedule, or news updates; it’s like having a personal helper available 24/7.
These AI agents learn from your behavior and preferences over time. For example, if you frequently request reminders about meetings, your assistant begins anticipating your needs, offering suggestions before you even ask. This makes technology feel more intuitive and personalized, saving you time and reducing stress in everyday tasks.
Virtual assistants are the perfect use case of how AI agents interact with humans in a way that feels natural and helpful. Their ability to understand language, interpret context, and respond accurately demonstrates the power of AI in making life simpler and more organized.
2. Recommendation Systems
AI agents power recommendation systems on platforms like Netflix, Spotify, and YouTube. They make recommendations for content based on your viewing, listening, and browsing preferences. This makes discovering new shows, songs, or videos quick and effortless.
These agents continuously learn from your behavior. The more you interact, the better their suggestions become, creating a personalized experience that feels tailored just for you. It’s a simple way AI makes everyday digital life smarter and more convenient.
3. Smart Home Devices
AI agents power smart home devices like thermostats, security cameras, and automated lights. They observe your routines and adjust settings such as temperature or lighting automatically to match your preferences. This makes everyday life more convenient without needing constant manual input.
These devices also enhance safety and energy efficiency. AI agents can optimize energy use and notify you of anomalous activity by learning from your habits, demonstrating how technology can make homes safer and smarter.
4. Customer Support Chatbots
AI-powered chatbots on websites and apps provide instant assistance to users. They answer common questions, guide visitors through processes, and help resolve issues without waiting for a human agent. This makes customer support faster and more efficient.
These AI agents learn from interactions to improve over time. The more they engage with users, the better they understand their needs and provide accurate responses. In some cases, businesses use AI consulting Services to shape chatbot capabilities so they not only respond accurately but also fit seamlessly into broader customer service strategies.
5. AI in eCommerce
AI agents help eCommerce platforms like Amazon recommend products based on your browsing and purchase history. They analyze patterns to suggest items you might need or enjoy, making online shopping faster and more personalized.
These agents also improve sales for businesses by predicting customer preferences and highlighting relevant products. This shows how AI can enhance shopping experiences while making recommendations smarter and more efficient.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
2. Why are AI Agents Important in AI Development?
AI agents are vital because they:
- Operate autonomously and make intelligent decisions.
- Improve efficiency and productivity.
- Improve user experiences and personalization.
- Solve complex problems in dynamic environments.
They power technologies like self-driving cars, virtual assistants, and automated customer support systems.
3. Are AI Agents and Bots the Same?
Not exactly. The differences are:
- Bots: Follow fixed scripts, limited decision-making.
- AI Agents: Adapt, learn, and act intelligently in dynamic situations.
In simple words, A chatbot answers questions based on scripts, while an AI agent can recommend products based on your preferences and past behavior.
Wrapping Up: Why Do AI Agents Matter?
AI agents can make everyday life and business operations easier by handling routine work, speeding up decisions, and creating more personalized experiences. Companies can improve efficiency and customer satisfaction through AI agent development, allowing teams to focus on innovation instead of repetitive tasks.
In 2026, Businesses can use AI agents to automate repetitive processes, enhance customer experiences, and make operations more efficient. Individuals can benefit by letting AI handle routine tasks, learning from AI insights, and focusing on what matters most.
The key is to identify the tasks that AI can handle effectively and start applying the right agents. Gradually, these systems can help solve real problems and make both work and daily life run smoothly.
Take advantage of AI Agents in 2026 to achieve efficient operations and delight your customers.








Share your thoughts about this blog!