Can a machine write stories, design images, or even compose music?
Just a few years ago, this sounded impossible.
Today, with the rise of Generative AI, it is becoming an everyday reality. This area of AI is expanding the capabilities of technology by creating human-like text as well as artwork and designs.
However, businesses are facing a new challenge: how to keep up with endless demands for fresh ideas, faster delivery, and personalized experiences. Generative AI is stepping in to fill this gap by not only automating tasks but also creating entirely new outputs.
McKinsey estimates that about 60% of companies are already experimenting with Gen AI in at least one business function, showing just how quickly it is being adopted.
So, what makes Generative AI stand out?
Traditional AI focuses on analyzing data and making predictions, while Generative AI technology creates entirely new content such as text, images, and code. This ability to generate original outputs is opening possibilities that once felt unimaginable for both businesses and creative industries.
In this blog, we will explore the definition, types, and applications of Generative AI across industries to provide a clear and practical overview.
Table of Contents
So let’s get hooked on our blog with the Generative AI definition!
What is Generative AI?
Generative AI (gen AI) is a field of artificial intelligence that focuses on creating new content instead of only analyzing existing data. It can generate text, images, code, audio, or even video by learning from large datasets and recognizing underlying patterns. Unlike traditional AI, which predicts or classifies, Generative AI produces original outputs that resemble human creativity.
Additionally, the rising use of Generative AI applications shows its growing impact. Businesses are turning to Generative AI models to produce content at scale, design prototypes, and even support decision-making. A PwC report states that AI technologies, including Generative AI, could add nearly $15.7 trillion to the global economy by 2030, highlighting why understanding Generative AI basics has become essential today.
Now that we know how it functions, let’s look at the different types of Generative AI models that make this possible.
How Does Generative AI Work?
Generative AI works by learning patterns from vast amounts of data and then producing new outputs based on that learning. It relies on advanced machine learning and deep learning models to analyze input data, recognize relationships, and generate content that appears original.
This process allows the AI to create text, images, audio, or other formats without directly copying the source material.
Key components of how Generative AI works include:
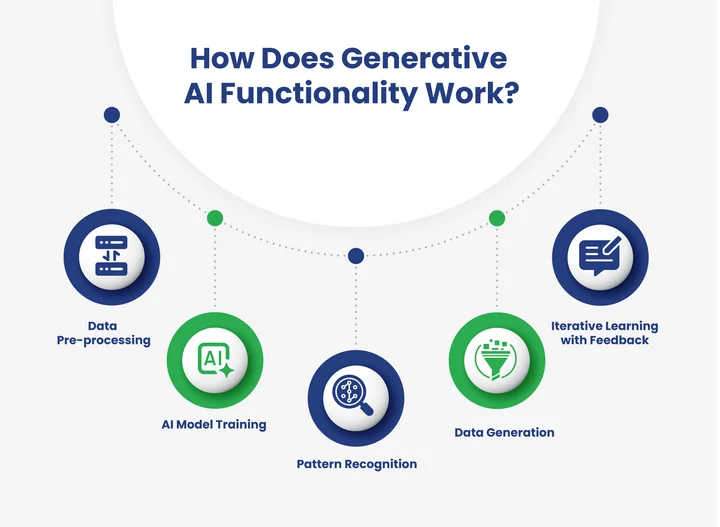
- Neural Networks: These simulate human brain functions to understand and process complex data patterns.
- Transformer Models and Large Language Models (LLMs): Used for understanding and generating human-like text.
- Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs): Comprise two models that compete to improve content generation quality.
- Diffusion and Autoencoder Models: Help in producing images, videos, and other complex outputs by learning data distribution.
Additionally, many Generative AI models rely on iterative learning, meaning they refine their outputs over time by comparing generated content with the training data.
For instance, text-based AI like ChatGPT predicts the next word in a sentence, a technique widely used in chatbot development, while image-based models such as Stable Diffusion create visuals from textual prompts.
This combination of learning, pattern recognition, and generation forms the core of Generative AI technology.
Turn wasted hours into breakthroughs? Generative AI can cut content and process time by up to 40% and generate new ideas for your team.
What are the Different Types of Generative AI?
Generative AI is not a single technology but a collection of models, each designed to create unique outputs from data. These models differ in how they learn, process information, and generate content, making them suitable for various applications like text creation, image generation, and even music composition.
It is essential to comprehend the various kinds to choose the appropriate model for a given task. Discuss the models:
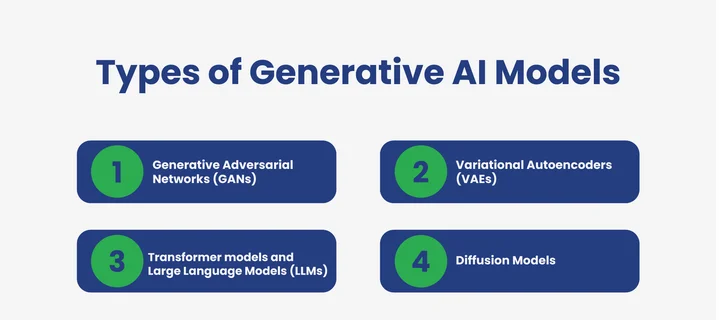
1. Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs)
Generative Adversarial Networks, or GANs, are made up of two models that work together: one creates content, and the other evaluates it. This back-and-forth improves the quality of the generated outputs over time. GANs are especially effective for producing realistic and high-quality content.
Some major highlights of GANs:
- Two-model system: The Generator produces content, and the discriminator checks authenticity.
- Content types: Images, videos, and virtual environments.
- Applications: AI-generated art, deepfake videos, and design prototypes.
- Industry use: Creative industries, marketing, gaming, and entertainment.
GANs demonstrate how Generative AI models can combine creativity and computation, creating outputs that closely resemble human-made content while saving time and resources.
2. Variational Autoencoders (VAEs)
Variational Autoencoders, or VAEs, create new content by learning the underlying patterns of existing data. They compress information and then reconstruct it, allowing the model to generate variations that feel original and meaningful.
This approach is particularly useful when structured or high-dimensional data is involved. In practice, VAEs are applied in areas such as image reconstruction, design variations, and data simulations.
For example, they can generate multiple creative versions of a product design or reconstruct medical images for research purposes. These models show how Generative AI technology can blend analytical precision with creative output, offering versatile solutions across industries.
3. Transformer models and Large Language Models (LLMs)
Transformer models and Large Language Models (LLMs) are designed to understand and generate human-like text. They work by analyzing the context of words and sentences and predicting what comes next to produce coherent and meaningful content. This makes them ideal for tasks that require natural language understanding and generation.
These models power tools like ChatGPT, enabling businesses and individuals to generate articles, answer questions, or even write code. Beyond text, large language models (LLMs) can assist in summarizing reports, creating conversational agents, and supporting customer interactions.
4. Diffusion Models
Diffusion models generate content by gradually refining random noise into meaningful outputs. They learn the patterns and structure of the data over multiple steps, which allows them to produce highly detailed and realistic results. This approach is particularly effective for visual content generation.
In practical use, diffusion models are widely applied in text-to-image generation, turning simple prompts into detailed visuals. Tools like Stable Diffusion showcase how diffusion models can transform simple prompts into:
- Artwork that resembles human-created designs
- Marketing visuals for campaigns, advertisements, and social media
- Design prototypes for products, packaging, or digital concepts
This demonstrates how Generative AI applications extend creativity and innovation across industries.
Each of these models powers unique capabilities, which businesses and industries are now putting to practical use.
How Do Generative AI Applications Shape Innovation Across Sectors?
Generative AI is transforming the way industries operate by enabling machines to create content, solve problems, and assist in decision-making. These applications, which range from simulations and predictive modeling to text and image generation, are assisting companies in innovating more quickly and effectively.
Companies across healthcare, marketing, entertainment, and research are leveraging these models to improve productivity and generate new opportunities.
Industries are discovering new ways to apply Generative AI. What does this look like in practice?
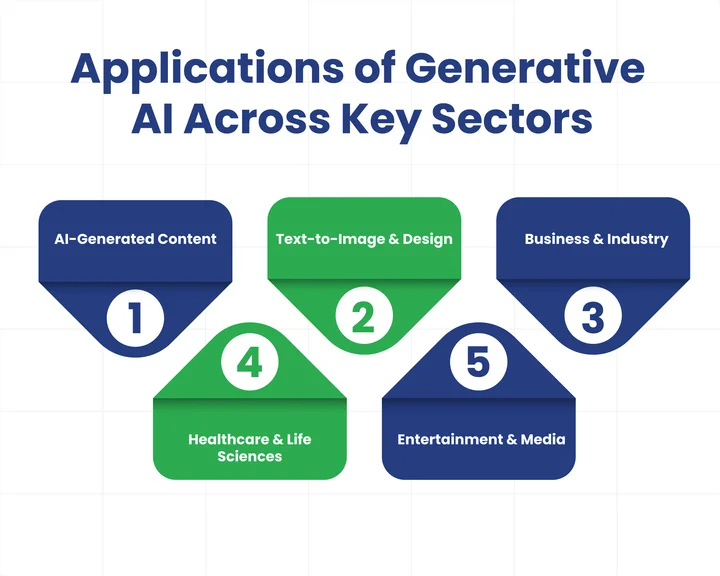
1. AI-Generated Content Creation
Generative AI is transforming content creation by producing human-like text for blogs, articles, marketing copy, and social media posts. These models can mimic different writing styles, maintain tone consistency, and generate content at scale, allowing businesses to meet growing content demands efficiently.
Additionally, AI-generated content helps teams focus on strategy and creativity rather than repetitive tasks. From drafting newsletters to creating product descriptions, Generative AI applications are becoming an essential tool for marketers and writers seeking faster, high-quality output.
2. Text-to-Image Generation and Visual Arts
Generative AI can turn simple text prompts into detailed and realistic images, illustrations, or concept art. This capability allows artists and designers to explore ideas rapidly, generate multiple variations, and visualize concepts that would take hours to produce manually.
Furthermore, these models support creative workflows by providing inspiration and reducing production time. Tools like Stable Diffusion enable professionals in marketing, design, and creative industries to generate visuals that align closely with project goals, demonstrating the power of text-to-image generation.
3. Generative AI in Business and Industry
Businesses leverage Generative AI to improve operations, develop prototypes, and explore innovative solutions. From automating reports to designing new products, these models help companies operate more efficiently while expanding their capacity for innovation.
Moreover, Generative AI applications assist in brainstorming ideas, simulating outcomes, and optimizing decision-making. Industries ranging from manufacturing to finance are experimenting with these tools to create practical solutions that save time and resources.
4. AI in Healthcare and Life Sciences
In healthcare, Generative AI supports tasks such as drug discovery, medical image analysis, and patient care simulations. By generating synthetic data and modeling outcomes, these technologies help researchers and clinicians test hypotheses faster and reduce manual workloads.
Additionally, AI applications assist in designing personalized treatment plans and predicting disease progression. Hospitals and research institutions increasingly rely on Generative AI technology to grow both operational efficiency and scientific innovation.
5. AI in Entertainment and Media
Generative AI is transforming the creation of stories, virtual characters, and interactive experiences in entertainment and media. It enables creators to experiment with narrative ideas, generate environments, and design assets efficiently, thereby accelerating the production process.
Furthermore, AI-powered tools support game development, content personalization, and media production at scale. By integrating Generative AI applications into creative workflows, media companies are exploring new ways to engage audiences and push the boundaries of imagination.
6. AI in Software Development and Coding
Generative AI is accelerating software development by assisting developers with code generation, debugging, documentation, and test creation. Examples include GitHub Copilot, Amazon CodeWhisperer, and Tabnine, which can suggest code snippets in real time, detect potential bugs, and streamline repetitive tasks.
These models allow developers to concentrate on architecture, performance, and innovation by automating repetitive coding tasks. They also speed up onboarding for new team members by generating clear explanations and documentation, making software development cycles faster and more efficient.
7. AI in Financial Services and Fintech
In financial services, Generative AI is being used to improve fraud detection, risk modeling, and customer experience. For example, Mastercard has piloted AI-driven fraud detection systems, and fintech companies like Upstart use AI models for credit scoring and loan decisions.
Generating synthetic data sets allows banks and fintech companies to test credit models without compromising real customer information. These tools also automate compliance documentation, create personalized financial advice, and power conversational assistants for customer support.
As a result, financial institutions can reduce operational costs, improve accuracy, and deliver more tailored products and services to clients.
Seeing its applications in action makes it clear why Generative AI brings significant advantages to businesses.
How Can Generative AI Benefit Your Business?
Generative AI is transforming the way businesses create content, make decisions, and engage with customers. Automating repetitive tasks and providing intelligent insights helps teams work smarter and unlock new opportunities.
These are the significant benefits:
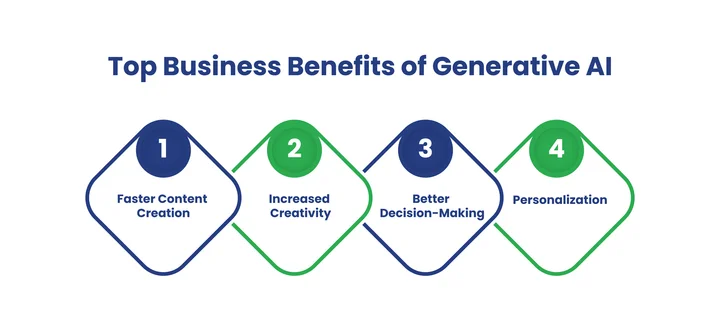
- Faster Content Creation: Speeds up text, image, and design generation, freeing creative teams for strategic work.
- Boost Creativity: Generates multiple variations and new ideas, helping creators explore concepts they might not imagine manually.
- Better Decision-Making: Provides AI-generated simulations and predictive models to support informed business decisions.
- Personalization: Enables tailored content, marketing campaigns, and user experiences by adapting outputs to individual preferences.
In short, Generative AI empowers businesses to work more efficiently, innovate continuously, and deliver experiences that truly resonate with their audience.
However, along with these benefits come important challenges that need careful management.
What Challenges Does Generative AI Bring to Businesses?
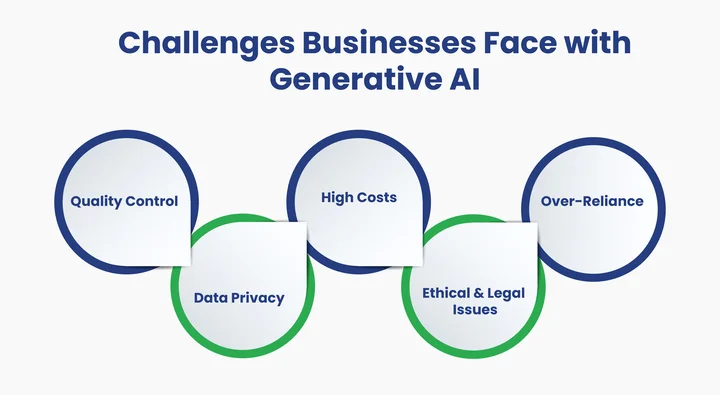
Generative AI offers exciting possibilities, but it also comes with challenges that businesses cannot ignore.
To use AI responsibly and effectively, it is crucial to comprehend and manage these challenges, which range from guaranteeing content quality to resolving ethical and legal issues.
Here’s a concise table of the main Gen AI challenges for businesses and how to address them:
| Factor | Challenge | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Quality Control | AI content may be inaccurate or biased. | Use human review, clear workflows, and retrain models on verified data. |
| Data Privacy | Sensitive data handling risks compliance issues. | Anonymize data, minimize usage, and choose certified vendors (ISO, GDPR). |
| Costs | AI systems can be expensive to implement. | Start with pilots, use cloud AI services, and budget for updates. |
| Integration | Difficult to merge AI with legacy systems. | Plan integration early, involve IT, and use APIs/middleware. |
| Ethical & Legal | Misuse or IP issues can arise. | Set policies, involve legal counsel, and track AI outputs. |
| Vendor Trust | Dependence on vendors may risk security or reliability. | Check vendor transparency, practices, and support. |
| Over-dependence | Excessive reliance can limit human creativity. | Treat AI as a co-pilot; retain human decision-making. |
Essentially, while Generative AI can help business operations, recognizing these challenges and proactively addressing them through strong governance, careful integration, and trusted vendors leads to smarter, safer, and more effective AI adoption.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
2. How is Generative AI used today?
Generative AI is everywhere:
- Writing blog posts, newsletters, or marketing content.
- Turning text prompts into images or illustrations.
- Designing product prototypes or virtual environments.
- Assisting healthcare research with simulations and data analysis.
3. What are the different types of Generative AI?
There are several popular models:
- GANs (Generative Adversarial Networks): Great for realistic images and videos.
- VAEs (Variational Autoencoders): Generate variations of existing data.
- Transformers & LLMs: Create human-like text for chatbots, articles, and more.
- Diffusion Models: Turn random noise into detailed visuals, used in tools like Stable Diffusion.
4. Will Generative AI replace human creativity?
Not entirely. Generative AI acts more like a creative partner. It can speed up idea generation, help visualize concepts, and handle repetitive tasks, but human judgment, imagination, and emotional insight are still irreplaceable. Think of it as strengthening, not replacing, human creativity.
The Bottom Line
In the end, Generative AI is changing the game for businesses everywhere. It helps businesses work more quickly, think more broadly, and provide experiences that genuinely connect, from producing text, images, and designs to assisting in more intelligent decision-making.
Businesses can scale creativity, turn creative ideas into reality, and maintain an advantage in a rapidly evolving market by investigating the best generative AI solutions.
Of course, the journey comes with challenges, but these are opportunities to grow smarter with technology. Implementing Generative AI thoughtfully opens doors to new possibilities, letting businesses create, experiment, and deliver value in ways that were unimaginable just a few years ago.
Your competitors are already moving faster! See how Generative AI can boost productivity by 30–50% and help you launch initiatives months sooner.








Share your thoughts about this blog!